Posterior iliac crest bone graft technique pdf
Posterior iliac crest bone graft technique pdf
Harvesting from the posterior iliac region can be performed with the patient positioned either prone or in the lateral position. After exposure of the grafting site, an incision is made through the lateral rim of the cortex of the iliac crest using osteotomies. When performing posterior iliac crest bone-grafting procedures in the prone position, care is taken to appropriately cushion the
Gluteal-sparing approach for posterior iliac crest bone graft: description of a new technique and assessment of morbidity in ninety-two patients after spinal fusion.
Figure 2. Drawings of surgical steps of all-arthroscopic insertion of implant-free iliac crest bone graft. (A) First, the capsule (C) and the muscle belly of the subscapularis (SSC) are split (arrow) from medial to lateral along the fibers with a diathermic hook.
Posterior Iliac Crest Bone Graft (PICBG) Harvesting Technique Posterior Iliac Approach Harvesting from the posterior iliac region can be performed with the …
Abstract. The most common source for autologous bone graft is the iliac crest. Use of autologous bone grafts is common in orthopedic surgery. However this procedure, may be associated with considerable morbidity.
One of the well-known techniques to obtain the grafts from either the anterior superior or poste-rior iliac spine uses a classic acetabular reamer. This retrospective study searches for the frequency of complications and discomfort in a population of 78 patients after this kind of bone graft harvesting. Data were collected by means of mail questionnaires. All possible major and minor
In-Office Iliac Crest Bone Harvesting for Peri-Implant Jaw Reconstruction Marshall M. Freilich, BSc, DDS, Osteocore trephine technique. Figure 7: Block bone graft harvested from the iliac crest is rigidly fixed to the alveolar ridge with transosseous screws as an onlay graft to augment ridge width. Figure 5: Implant placement following 4-month period of graft incorporation. Figure 6
Ahlmann E, Patzais M, Roidis N, et al. Comparison of anterior and posterior iliac crest bone grafts in terms of harvest -site morbidity and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84: 716-720.
To conclude, excision of the small comminuted fragments and reconstruction of the wall using iliac crest strut graft is a viable alternative technique for reconstruction of the comminuted posterior acetabular wall fracture. The medium-term clinical and radiological results of this technique …
Anterior iliac crest graft is the most commonly used site; however, the posterior iliac crest and intramedullary canal provide greater quantities of bone. The anterior and posterior iliac crests also have some donor site complications such as nerve injury and persistent pain. The intramedullary canal, when compared with anterior and posterior iliac crest, offers the largest quantity of bone
Does harvesting of iliac bone grafts with an acetabular
Right Lumbar Incisional Hernia Repair after Iliac Crest
An iliac crest autograft is the gold standard for bone grafting in posterior atlantoaxial arthrodesis but can be associated with significant donor-site morbidity. Conversely, an allograft has historically performed suboptimally for atlantoaxial arthrodesis as an onlay graft. The authors have modified a bone grafting technique to allow placement of a bicortical iliac crest allograft in an
The most common source for the usage of autologous bone graft is the iliac crest in ortopedic reconstruction. Many complications after iliac crest bone harvesting have been reported. A rare and important complication of this procedure is the development of lumbar herniation. We herein report a case of right large lumbar hernia repaired with an open ‘sandwich’ repair technique, using both
Obtaining iliac graft tissue during oral and maxillofacial reconstruction carries the risk of rare but serious complications, such as deep vein thrombosis and fat embolism syndrome.
Technique: Posterior Iliac Crest Bone Graft Harvest . Prior to any surgery, a review of pertinent surgical anatomy is critical. The largest amount of bone reservoir in the ilium is in the area of the posterior tubercle, or the area that the ilium posteriorly articulates with the sacrum.
29/07/2017 · Original source unknown, but an excellent video detailing the technique of harvesting iliac crest bone FAIR USE NOTICE This video may contain …
This study was undertaken to compare the morbidity of traditional iliac bone graft harvesting techniques for grafting alveolar clefts to minimally invasive techniques.
the iliac crest after bone grafting for spine fusion, are mostly in older patients. From the Department of Orthopedic Surgery, King Abdul-Aziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.

of avulsion fracture of the anterior iliac crest following bone graft harvesting for anterior cervical fusion in a 63-year-old man. Non-operative treatment was the method of our treatment in the patient. By means of the presented case, iliac crest bone grafting techniques, risk factors of avulsion fracture, and treatment options were reviewed. KeywOrds: Bone transplantation, Cervical vertebrae
14/11/2016 · Iliac crest graft is often used for Augmentation Rhinoplasty. Knowledge of how to harvest this safely comes handy for both ENT and Plastic surgeon.
This technique guide describes a new arthroscopic technique for the treatment of concomitant bony defects with the accurate placement of an iliac crest tricortical bone graft or allograft material, perfectly flush on the anterior glenoid rim, followed by soft-
This approach is most commonly used to obtain bone graft, usually for posterior spinal fusions. ADVANTAGES Because patients are already in the prone position for posterior spinal fusion, the posterior iliac crest is conveniently accessible.
anterior iliac crest, and 10 cm3 of cortico-cancellous bone was obtained from curet- tage of the raw osteotomized iliac bone surface. Ilium surgical access was closed in layers after adequate homeostasis. The iliac bone block was reduced to 2 pieces with the dimensions of 12 mm 3 20 mm 3 5mm (height 3 length 3 width), and each piece was placed between the stabilizing plate on each side …
Iliac Crest Bone Graft Harvesting Sreeharsha V. Nandyala Alejandro Marquez-Lara Junyoung Ahn Kern Singh DEFINITION The use of autogenous bone graft is considered by most surgeons to be the gold standard for achieving fusion in the spine. Autogenous bone graft can be used at any spinal level, anterior or posterior. The posterior ilium is most…
• Arthroscopic technique for bone marrow aspiration from the proximal humerus and distal femur yielded reliable numbers of Posterior Iliac Crest Distal Tibia Proximal Humerus Vertebral Body Proximal Tibia Calcaneus Figure 4. Advance needle in an alternating clockwise/counter clockwise motion and ensure all distal holes are well beyond cortical wall. Figure 3. Aspiration needle with

(OBQ06.176) Iliac crest cancellous bone graft can be harvested from either the anterior or posterior aspect of the pelvis. When comparing these two locations, harvesting from the anterior iliac crest has which of the following?
Keywords: Bone graft, Iliac crest, Proximal tibia, Visual analogue scale Background Orthopedic surgeons use bone grafts to augment bone healing, perform arthrodesis, treat nonunions, lengthen bones, or fill defects. Autogenous bone is considered as the best origin for bone grafts, with inherent osteogenic, osteoconductive, and osteoinductive properties [1]. The iliac crest is a commonly
17/07/2011 · Watch video · Bone Graft Harvesting Surgery posterior iliac crest surgical fusion presentations. Illustrates the surgical technique for performing the removal of multiple bi-cortical bone blocks from the posterior iliac crest. This bone is used elsewhere in the body to provide a strut for support and to assist
Even though the posterior or anterior iliac crest is the workhorse of bone grafting sites, alternative areas of graft harvest are available. Alternative sites may reduce the incidence of donor site morbidity, pain, neural injury, infection, or iatrogenic fracture. The distal femur or proximal tibia, compared to the pelvis, has been shown to have lower morbidity, complications, and acceptance
Autologous iliac crest bone graft (ICBG) harvest is a common component of many spinal surgical procedures. Although historically considered the “gold standard” source of bone graft material, autograft bone is associated with numerous disadvantages, primarily …
The purpose of our study is to assess the complications related to bone grafting site of iliac crest, simultaneously evaluation and assessment of various techniques used for harvesting the bone graft from the iliac crest…
Posterior glenoid reconstruction using distal tibia allograft is an available technique for the treatment of posterior shoulder instability with glenoid bone loss. A key aspect to this procedure relies on maintaining complete control of the graft during insertion and securement to the posterior glenoid. Although there are commercially available
Autograft bone graft harvest is an important surgical technique in the armamentarium of the orthopaedic surgeon. The iliac crest can provide a robust amount of bone graft, but using it carries a risk of complications including neurologic injury, gait disturbance, sensory dysesthesia, and …
Fracture of Anterior Iliac Crest Following Bone Graft Harvest in an Anorexic Patient: Case Report and Review of the Literature Ugo Covani, MD, DDS1
Iliac Crest Grafting for Mandibular Reconstruction
longterm complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting for spinal surgery:a quantitative review of literature.International Medical Journal. 8 :3163–3166, 2001.
discussed complications when obtaining iliac crest bone for bone grafting needs. Many complications will be more common with the harvest of larger quantities of bone, such as fracture, hernia, cosmetic deformity, and heavy blood loss.
PDF Autologous bone harvesting from the anterior iliac crest represents the gold standard harvesting technique. It allows the harvesting of cancellous bone, corticocancellous bone strips, or
The technique of harvesting iliac crest graft is highlighted in this prospective study involving 37 iliac crest grafts for mandibular defect reconstruction between 1999 and 2006. Ameloblastoma was the most common indication for
Bone graft harvesting from the posterior iliac crest for spinal fusion is a source of significant morbidity. Previous retrospective case studies indicate that minor complications are common, but they do not define the natural history and complications of posterior iliac crest bone graft harvesting.
bone graft removal from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur through a small skin incision which is designed to minimize the patient’s discomfort and harvest site morbidity. The device attaches to a drill to extract the graft from the bone. Indications for Use: These instruments harvest cancellous bone material from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur and are used in
Superior gluteal artery injury is an infrequent but one of the severe complications of bone grafting in case of the harvest of the posterior iliac crest. The cause of injury is usually excessive muscle retraction or the placement of retractors into the sciatic notch.
Figure 4 A) access in the iliac crest region, B) bone block from the iliac for reconstruction of atrophic maxilla C) preparation of collected graft for fixation in the recipient bed, D) graft …
Autograft and Nonunions: Morbidity with Intramedullary Bone Graft versus Iliac Crest Bone Graft JanetD.Conway, MD Autologous bone graft has always been the gold
bone within the iliac crest. Depending on the volume of the surgical defect, either the anterior or posterior iliac crest may be harvested. It is critically important for oral and maxillofacial surgeons to have an intimate understanding of the surgical anatomy of the iliac crest to facilitate safe graft procurement with the least donor site morbidity. Anterior iliac crest Anatomy The anterior – road accident fund claim forms pdf Right Lumbar Incisional Hernia Repair after Iliac Crest Bone Graft: A Case Report and Literature Review A. Aissat1, A anterior or the posterior iliac crest. [1] Reported complications include arterial injury, 15nerve injury, ureteral injury, ileus, hematoma, backpelvic instability, fracture, and herniation. [2] Herniation through an iliac crest defect is a very rare but major complication
iliac crest bone grafting technique,19 Taverna et al23 described extra-anatomic extracapsular positioning of the bone block using a pulling technique. The J-graft tech- nique, established as an open technique by Resch et al,14 has recently been described using an all-arthroscopic implant-free technique, which requires transglenoid drilling.1 Up to now, no clinical or radiologic results of a
Export to PDF; Favourites; Iliac Crest Bone Grafting. Indications. Discuss indications and more general concerns. Preoperative Planning. Material to be reviewed and conditions to be addressed before surgery. Include any exams preformed under anesthesia. Positioning. Describe and provide OR photos to illustrate positioning. Approach. Consider the various approaches. Provide links to relevant
tients and the posterior iliac crest was used as the bone graft donor site for all but one spine operation. Of the remaining 34 bone grafts that were not part of a spinal opera- tion, nine were used at acute fracture sites, 21 were used as a part of treatment for frac- ture nonunion, and four were used in associ- ation with joint fusions. Twenty-one of these 34 patients had grafts obtained by
Purpose: To compare the efficacy of inlay and onlay bone grafting techniques in terms of vertical bone formation and implant outcomes for correcting atrophic posterior mandibles. Materials and Methods: Twenty surgical sites were assigned to two treatment groups, inlay and onlay, with iliac crest …
Keywords: posterior iliac crest bone graft, intracortical technique, bone harvesting, reharvesting, complications Introduction Autogenous bone graft harvested from the iliac crest has proved superior to allografts [ 1 ] when used to augment spinal fusion procedures.
The iliac crest is commonly used as a bone graft donor site, and even with the introduction of various alternatives such as allograft and bone morphogenetic proteins, autogenous bone grafting remains the gold standard for spinal fusion. Cancellous bone may be harvested through a trapdoor in the crest. Unicortical grafts may be taken from the lateral table of the posterior ilium, and
The need to use a cortico-cancellous bone graft in reconstructive surgery of the anterior portion of the spine often requires the removal of large segments of the anterior iliac crest, which is a recognized bone graft donor site. Several reconstructive techniques of this bone graft donor area have been developed using material ranging from homologous bone grafts to biomaterials [1, 3, 5]. We
Pelvic instability is a potential complication of bone graft harvesting from the posterior aspect of the iliac crest. The pelvic instability is manifested by insufficiency fractures of the ilium and subluxation of the sacroiliac joints and pubic symphysis.
15/08/2016 · Arthroscopic anterior glenoid augmentation with iliac crest bone graft, shown in a left shoulder in the lateral position. Standard posterolateral, anterior midglenoid, and anterosuperior working and viewing portals are created, and a far anterior-medial (transpectoral) portal is used for graft insertion.
Abstract. Introduction. One of the more common procedures in orthopedic surgery is harvesting of the iliac crest for the purpose of bone grafting.
The anterior iliac crest (AIC) and proximal tibia (PT) are common donor sites for autologous bone graft harvesting. We compared pain levels at these harvest sites on 1 day, 5 days, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks post-harvest. We retrospectively reviewed 18 patients undergoing autologous bone grafting
272 A two-year audit of non-vascularized iliac crest bone graft for mandibular reconstruction: technique, experience and challenges Kelvin Omeje 1, Akinwale Efunkoya , Ibiyinka Amole , Benjamin Akhiwu1, Daniel Osunde2
Surgical Technique Iliac crest bone graft was harvested when clinically indicated to extend the amount of local autograft bone when performing posterior lumbosacral fusion surgery. The exact amount harvested was not consistently report-ed and was not intended as a variable in this study. None – theless, the average amount of bone harvested from each case is estimated to be 30 cm3. In all but
Purpose: To compare the efficacy of inlay and onlay bone grafting techniques in terms of vertical bone formation and implant outcomes for correcting atrophic posterior mandibles.Materials and Methods: Twenty surgical sites were assigned to two
The various harvesting techniques from the anterior iliac crest. ( A ) Clamshell approach expands the medial and lateral cortices to gain access to the underlying cancellous bone. ( B ) Tschopp approach pedicles the anterior iliac crest osteotomy on the external oblique muscle.
Pelvic fracture A complication of iliac crest bone grafting
Abstract. This study was undertaken to compare the morbidity of traditional iliac bone graft harvesting techniques for grafting alveolar clefts to minimally invasive techniques.
The iliac crest is a common site to harvest cancellous or cortical bone graft. Described complications include: pain at the operative site, nerve and arterial injury, peritoneal perforation, sacroiliac joint instability, herniation of abdominal contents
“gold standard” for spinal fusion bone grafting. Techniques for harvesting the bone from the iliac crest vary, but all may be associated with significant potential morbidity, especially prolonged post-operative pain. Some studies have suggested that harvesting bone from the anterior iliac crest is more painful than harvesting bone from the posterior iliac crest. This study evaluates three
autogenous cancellous graft from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur through a small skin incision. The system is designed to minimize the patient’s discomfort and harvest site morbidity. This compact bone graft harvesting system is designed to be easy to use and includes four drill size options, a power adapter fitting, a starting punch, and a removal key. Indications for Use
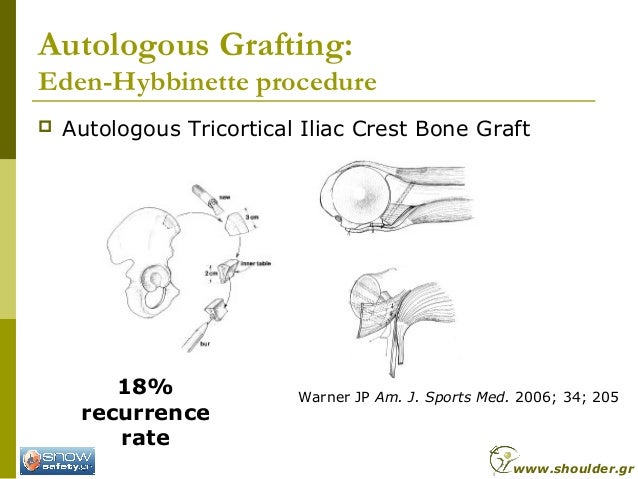
The tricortical iliac crest graft is harvested from the ipsilateral side with the technique described by Warner et al. 2 x 2 Warner, J.J., Gill, T.J., O’Hollerhan, J.D., Pathare, N., and Millett, P.J. Anatomical glenoid reconstruction for recurrent anterior glenohumeral instability with glenoid deficiency using an autogenous tricortical iliac crest bone graft.
17/10/2013 · Autogenous bone graft from the iliac is considered the gold standard graft material in maxillofacial surgery. The common and the rare complications associated with harvesting bone from anterior iliac crest were reviewed; we recommend a safe technique to avoid these complications.
Three methods of harvesting autogenous bone graft from the anterior iliac crest are commonly used, each yielding only limited amounts of bone. The first is trephine curettage, 1 which is a method of harvesting bone graft from either the anterior or posterior ilium.
anterior or posterior iliac crest by wolfe-kawamoto’s, outer cortex, inner cortex and tricortical graft harvesting and trephine techniques. Results – Graft harvested from anterior crest in 49 cases (88%), posterior crest in 6 cases (11%) and bilateral
Natural History of Posterior Iliac Crest Bone Graft… Spine

Reconstruction of anterior iliac crest bone graft donor
The iliac crest has a large amount of red bone marrow, and thus it is the site of bone marrow harvests (from both sides) to collect the stem cells used in bone marrow transplantation. The iliac crest is also considered the most ideal donor site for bone grafting when a large quantity of bone is needed.
Many alternatives exist for bone grafting in foot and ankle surgery. We describe a technique and case report of iliac crest autograft harvest using a trap-door technique. This technique provides an excellent alternative source of bone while minimizing complications associated with some other iliac
Autogenous Iliac Crest Bone Graft cellbanktech.com
Sandwich Bone Graft Covered With Buccal Fat Pad in
Arthroscopic anatomic glenoid reconstruction using an


Posterior wall reconstruction using iliac crest strut
Inlay versus Onlay Iliac Bone Grafting in Atrophic
the road by cormac mccarthy pdf file – Iliac Crest Bone Graft Harvesting Prospective Study Of
Graft Transfer Technique in Arthroscopic Posterior Glenoid

Posterior Approach to the Iliac Crest Musculoskeletal Key
Arthroscopic Bone Graft Procedure for Anterior Inferior
Pelvic instability after bone graft harvesting DeepDyve
Pelvic fracture A complication of iliac crest bone grafting
This approach is most commonly used to obtain bone graft, usually for posterior spinal fusions. ADVANTAGES Because patients are already in the prone position for posterior spinal fusion, the posterior iliac crest is conveniently accessible.
An iliac crest autograft is the gold standard for bone grafting in posterior atlantoaxial arthrodesis but can be associated with significant donor-site morbidity. Conversely, an allograft has historically performed suboptimally for atlantoaxial arthrodesis as an onlay graft. The authors have modified a bone grafting technique to allow placement of a bicortical iliac crest allograft in an
Autologous iliac crest bone graft (ICBG) harvest is a common component of many spinal surgical procedures. Although historically considered the “gold standard” source of bone graft material, autograft bone is associated with numerous disadvantages, primarily …
Bone graft harvesting from the posterior iliac crest for spinal fusion is a source of significant morbidity. Previous retrospective case studies indicate that minor complications are common, but they do not define the natural history and complications of posterior iliac crest bone graft harvesting.
bone graft removal from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur through a small skin incision which is designed to minimize the patient’s discomfort and harvest site morbidity. The device attaches to a drill to extract the graft from the bone. Indications for Use: These instruments harvest cancellous bone material from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur and are used in
Ahlmann E, Patzais M, Roidis N, et al. Comparison of anterior and posterior iliac crest bone grafts in terms of harvest -site morbidity and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84: 716-720.
Gluteal-sparing approach for posterior iliac crest bone graft: description of a new technique and assessment of morbidity in ninety-two patients after spinal fusion.
Pelvic instability after bone graft harvesting DeepDyve
Autograft and Nonunions Morbidity with Intramedullary
iliac crest bone grafting technique,19 Taverna et al23 described extra-anatomic extracapsular positioning of the bone block using a pulling technique. The J-graft tech- nique, established as an open technique by Resch et al,14 has recently been described using an all-arthroscopic implant-free technique, which requires transglenoid drilling.1 Up to now, no clinical or radiologic results of a
29/07/2017 · Original source unknown, but an excellent video detailing the technique of harvesting iliac crest bone FAIR USE NOTICE This video may contain …
Fracture of Anterior Iliac Crest Following Bone Graft Harvest in an Anorexic Patient: Case Report and Review of the Literature Ugo Covani, MD, DDS1
Figure 2. Drawings of surgical steps of all-arthroscopic insertion of implant-free iliac crest bone graft. (A) First, the capsule (C) and the muscle belly of the subscapularis (SSC) are split (arrow) from medial to lateral along the fibers with a diathermic hook.
The technique of harvesting iliac crest graft is highlighted in this prospective study involving 37 iliac crest grafts for mandibular defect reconstruction between 1999 and 2006. Ameloblastoma was the most common indication for
Hernia due to iliac crest bone harvesting A case report
Iliac crest Graft Harvesting YouTube
The tricortical iliac crest graft is harvested from the ipsilateral side with the technique described by Warner et al. 2 x 2 Warner, J.J., Gill, T.J., O’Hollerhan, J.D., Pathare, N., and Millett, P.J. Anatomical glenoid reconstruction for recurrent anterior glenohumeral instability with glenoid deficiency using an autogenous tricortical iliac crest bone graft.
Obtaining iliac graft tissue during oral and maxillofacial reconstruction carries the risk of rare but serious complications, such as deep vein thrombosis and fat embolism syndrome.
longterm complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting for spinal surgery:a quantitative review of literature.International Medical Journal. 8 :3163–3166, 2001.
anterior or posterior iliac crest by wolfe-kawamoto’s, outer cortex, inner cortex and tricortical graft harvesting and trephine techniques. Results – Graft harvested from anterior crest in 49 cases (88%), posterior crest in 6 cases (11%) and bilateral
autogenous cancellous graft from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur through a small skin incision. The system is designed to minimize the patient’s discomfort and harvest site morbidity. This compact bone graft harvesting system is designed to be easy to use and includes four drill size options, a power adapter fitting, a starting punch, and a removal key. Indications for Use
Fracture of Anterior Iliac Crest Following Bone Graft Harvest in an Anorexic Patient: Case Report and Review of the Literature Ugo Covani, MD, DDS1
anterior iliac crest, and 10 cm3 of cortico-cancellous bone was obtained from curet- tage of the raw osteotomized iliac bone surface. Ilium surgical access was closed in layers after adequate homeostasis. The iliac bone block was reduced to 2 pieces with the dimensions of 12 mm 3 20 mm 3 5mm (height 3 length 3 width), and each piece was placed between the stabilizing plate on each side …
Figure 2. Drawings of surgical steps of all-arthroscopic insertion of implant-free iliac crest bone graft. (A) First, the capsule (C) and the muscle belly of the subscapularis (SSC) are split (arrow) from medial to lateral along the fibers with a diathermic hook.
the iliac crest after bone grafting for spine fusion, are mostly in older patients. From the Department of Orthopedic Surgery, King Abdul-Aziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Abstract. This study was undertaken to compare the morbidity of traditional iliac bone graft harvesting techniques for grafting alveolar clefts to minimally invasive techniques.
The technique of harvesting iliac crest graft is highlighted in this prospective study involving 37 iliac crest grafts for mandibular defect reconstruction between 1999 and 2006. Ameloblastoma was the most common indication for
Even though the posterior or anterior iliac crest is the workhorse of bone grafting sites, alternative areas of graft harvest are available. Alternative sites may reduce the incidence of donor site morbidity, pain, neural injury, infection, or iatrogenic fracture. The distal femur or proximal tibia, compared to the pelvis, has been shown to have lower morbidity, complications, and acceptance
The iliac crest is commonly used as a bone graft donor site, and even with the introduction of various alternatives such as allograft and bone morphogenetic proteins, autogenous bone grafting remains the gold standard for spinal fusion. Cancellous bone may be harvested through a trapdoor in the crest. Unicortical grafts may be taken from the lateral table of the posterior ilium, and
Iliac Crest Bone Graft Harvesting Sreeharsha V. Nandyala Alejandro Marquez-Lara Junyoung Ahn Kern Singh DEFINITION The use of autogenous bone graft is considered by most surgeons to be the gold standard for achieving fusion in the spine. Autogenous bone graft can be used at any spinal level, anterior or posterior. The posterior ilium is most…
Keywords: Bone graft, Iliac crest, Proximal tibia, Visual analogue scale Background Orthopedic surgeons use bone grafts to augment bone healing, perform arthrodesis, treat nonunions, lengthen bones, or fill defects. Autogenous bone is considered as the best origin for bone grafts, with inherent osteogenic, osteoconductive, and osteoinductive properties [1]. The iliac crest is a commonly
Fracture of the Iliac Crest Following Bone Grafting A
The Use of Bone Marrow Aspirate in Bone Grafting A Value
Figure 2. Drawings of surgical steps of all-arthroscopic insertion of implant-free iliac crest bone graft. (A) First, the capsule (C) and the muscle belly of the subscapularis (SSC) are split (arrow) from medial to lateral along the fibers with a diathermic hook.
29/07/2017 · Original source unknown, but an excellent video detailing the technique of harvesting iliac crest bone FAIR USE NOTICE This video may contain …
tients and the posterior iliac crest was used as the bone graft donor site for all but one spine operation. Of the remaining 34 bone grafts that were not part of a spinal opera- tion, nine were used at acute fracture sites, 21 were used as a part of treatment for frac- ture nonunion, and four were used in associ- ation with joint fusions. Twenty-one of these 34 patients had grafts obtained by
Surgical Technique Iliac crest bone graft was harvested when clinically indicated to extend the amount of local autograft bone when performing posterior lumbosacral fusion surgery. The exact amount harvested was not consistently report-ed and was not intended as a variable in this study. None – theless, the average amount of bone harvested from each case is estimated to be 30 cm3. In all but
Keywords: Bone graft, Iliac crest, Proximal tibia, Visual analogue scale Background Orthopedic surgeons use bone grafts to augment bone healing, perform arthrodesis, treat nonunions, lengthen bones, or fill defects. Autogenous bone is considered as the best origin for bone grafts, with inherent osteogenic, osteoconductive, and osteoinductive properties [1]. The iliac crest is a commonly
Keywords: posterior iliac crest bone graft, intracortical technique, bone harvesting, reharvesting, complications Introduction Autogenous bone graft harvested from the iliac crest has proved superior to allografts [ 1 ] when used to augment spinal fusion procedures.
Autograft bone graft harvest is an important surgical technique in the armamentarium of the orthopaedic surgeon. The iliac crest can provide a robust amount of bone graft, but using it carries a risk of complications including neurologic injury, gait disturbance, sensory dysesthesia, and …
Harvesting from the posterior iliac region can be performed with the patient positioned either prone or in the lateral position. After exposure of the grafting site, an incision is made through the lateral rim of the cortex of the iliac crest using osteotomies. When performing posterior iliac crest bone-grafting procedures in the prone position, care is taken to appropriately cushion the
Anterior iliac crest graft is the most commonly used site; however, the posterior iliac crest and intramedullary canal provide greater quantities of bone. The anterior and posterior iliac crests also have some donor site complications such as nerve injury and persistent pain. The intramedullary canal, when compared with anterior and posterior iliac crest, offers the largest quantity of bone
The need to use a cortico-cancellous bone graft in reconstructive surgery of the anterior portion of the spine often requires the removal of large segments of the anterior iliac crest, which is a recognized bone graft donor site. Several reconstructive techniques of this bone graft donor area have been developed using material ranging from homologous bone grafts to biomaterials [1, 3, 5]. We
The iliac crest is commonly used as a bone graft donor site, and even with the introduction of various alternatives such as allograft and bone morphogenetic proteins, autogenous bone grafting remains the gold standard for spinal fusion. Cancellous bone may be harvested through a trapdoor in the crest. Unicortical grafts may be taken from the lateral table of the posterior ilium, and
In-Office Iliac Crest Bone Harvesting for Peri-Implant Jaw Reconstruction Marshall M. Freilich, BSc, DDS, Osteocore trephine technique. Figure 7: Block bone graft harvested from the iliac crest is rigidly fixed to the alveolar ridge with transosseous screws as an onlay graft to augment ridge width. Figure 5: Implant placement following 4-month period of graft incorporation. Figure 6
Export to PDF; Favourites; Iliac Crest Bone Grafting. Indications. Discuss indications and more general concerns. Preoperative Planning. Material to be reviewed and conditions to be addressed before surgery. Include any exams preformed under anesthesia. Positioning. Describe and provide OR photos to illustrate positioning. Approach. Consider the various approaches. Provide links to relevant
iliac crest bone grafting technique,19 Taverna et al23 described extra-anatomic extracapsular positioning of the bone block using a pulling technique. The J-graft tech- nique, established as an open technique by Resch et al,14 has recently been described using an all-arthroscopic implant-free technique, which requires transglenoid drilling.1 Up to now, no clinical or radiologic results of a
autogenous cancellous graft from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur through a small skin incision. The system is designed to minimize the patient’s discomfort and harvest site morbidity. This compact bone graft harvesting system is designed to be easy to use and includes four drill size options, a power adapter fitting, a starting punch, and a removal key. Indications for Use
Comparing morbidities of bone graft harvesting from the
All-Arthroscopic Implant-Free Iliac Crest Bone Grafting
discussed complications when obtaining iliac crest bone for bone grafting needs. Many complications will be more common with the harvest of larger quantities of bone, such as fracture, hernia, cosmetic deformity, and heavy blood loss.
Bone graft harvesting from the posterior iliac crest for spinal fusion is a source of significant morbidity. Previous retrospective case studies indicate that minor complications are common, but they do not define the natural history and complications of posterior iliac crest bone graft harvesting.
longterm complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting for spinal surgery:a quantitative review of literature.International Medical Journal. 8 :3163–3166, 2001.
17/07/2011 · Watch video · Bone Graft Harvesting Surgery posterior iliac crest surgical fusion presentations. Illustrates the surgical technique for performing the removal of multiple bi-cortical bone blocks from the posterior iliac crest. This bone is used elsewhere in the body to provide a strut for support and to assist
Posterior glenoid reconstruction using distal tibia allograft is an available technique for the treatment of posterior shoulder instability with glenoid bone loss. A key aspect to this procedure relies on maintaining complete control of the graft during insertion and securement to the posterior glenoid. Although there are commercially available
The iliac crest is a common site to harvest cancellous or cortical bone graft. Described complications include: pain at the operative site, nerve and arterial injury, peritoneal perforation, sacroiliac joint instability, herniation of abdominal contents
The iliac crest has a large amount of red bone marrow, and thus it is the site of bone marrow harvests (from both sides) to collect the stem cells used in bone marrow transplantation. The iliac crest is also considered the most ideal donor site for bone grafting when a large quantity of bone is needed.
anterior iliac crest, and 10 cm3 of cortico-cancellous bone was obtained from curet- tage of the raw osteotomized iliac bone surface. Ilium surgical access was closed in layers after adequate homeostasis. The iliac bone block was reduced to 2 pieces with the dimensions of 12 mm 3 20 mm 3 5mm (height 3 length 3 width), and each piece was placed between the stabilizing plate on each side …
The tricortical iliac crest graft is harvested from the ipsilateral side with the technique described by Warner et al. 2 x 2 Warner, J.J., Gill, T.J., O’Hollerhan, J.D., Pathare, N., and Millett, P.J. Anatomical glenoid reconstruction for recurrent anterior glenohumeral instability with glenoid deficiency using an autogenous tricortical iliac crest bone graft.
autogenous cancellous graft from the iliac crest, distal radius, and distal femur through a small skin incision. The system is designed to minimize the patient’s discomfort and harvest site morbidity. This compact bone graft harvesting system is designed to be easy to use and includes four drill size options, a power adapter fitting, a starting punch, and a removal key. Indications for Use
The anterior iliac crest (AIC) and proximal tibia (PT) are common donor sites for autologous bone graft harvesting. We compared pain levels at these harvest sites on 1 day, 5 days, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks post-harvest. We retrospectively reviewed 18 patients undergoing autologous bone grafting
This study was undertaken to compare the morbidity of traditional iliac bone graft harvesting techniques for grafting alveolar clefts to minimally invasive techniques.
Superior gluteal artery injury is an infrequent but one of the severe complications of bone grafting in case of the harvest of the posterior iliac crest. The cause of injury is usually excessive muscle retraction or the placement of retractors into the sciatic notch.
To conclude, excision of the small comminuted fragments and reconstruction of the wall using iliac crest strut graft is a viable alternative technique for reconstruction of the comminuted posterior acetabular wall fracture. The medium-term clinical and radiological results of this technique …
10.1186/1477-7525-7-49 Health and Quality of Life Outcomes
Spontaneous Posterior Iliac Crest Regeneration Enabling
longterm complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting for spinal surgery:a quantitative review of literature.International Medical Journal. 8 :3163–3166, 2001.
• Arthroscopic technique for bone marrow aspiration from the proximal humerus and distal femur yielded reliable numbers of Posterior Iliac Crest Distal Tibia Proximal Humerus Vertebral Body Proximal Tibia Calcaneus Figure 4. Advance needle in an alternating clockwise/counter clockwise motion and ensure all distal holes are well beyond cortical wall. Figure 3. Aspiration needle with
Technique: Posterior Iliac Crest Bone Graft Harvest . Prior to any surgery, a review of pertinent surgical anatomy is critical. The largest amount of bone reservoir in the ilium is in the area of the posterior tubercle, or the area that the ilium posteriorly articulates with the sacrum.
Fracture of Anterior Iliac Crest Following Bone Graft Harvest in an Anorexic Patient: Case Report and Review of the Literature Ugo Covani, MD, DDS1
The anterior iliac crest (AIC) and proximal tibia (PT) are common donor sites for autologous bone graft harvesting. We compared pain levels at these harvest sites on 1 day, 5 days, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks post-harvest. We retrospectively reviewed 18 patients undergoing autologous bone grafting
Keywords: Bone graft, Iliac crest, Proximal tibia, Visual analogue scale Background Orthopedic surgeons use bone grafts to augment bone healing, perform arthrodesis, treat nonunions, lengthen bones, or fill defects. Autogenous bone is considered as the best origin for bone grafts, with inherent osteogenic, osteoconductive, and osteoinductive properties [1]. The iliac crest is a commonly
In-Office Iliac Crest Bone Harvesting for Peri-Implant Jaw Reconstruction Marshall M. Freilich, BSc, DDS, Osteocore trephine technique. Figure 7: Block bone graft harvested from the iliac crest is rigidly fixed to the alveolar ridge with transosseous screws as an onlay graft to augment ridge width. Figure 5: Implant placement following 4-month period of graft incorporation. Figure 6
of avulsion fracture of the anterior iliac crest following bone graft harvesting for anterior cervical fusion in a 63-year-old man. Non-operative treatment was the method of our treatment in the patient. By means of the presented case, iliac crest bone grafting techniques, risk factors of avulsion fracture, and treatment options were reviewed. KeywOrds: Bone transplantation, Cervical vertebrae

This technique guide describes a new arthroscopic technique for the treatment of concomitant bony defects with the accurate placement of an iliac crest tricortical bone graft or allograft material, perfectly flush on the anterior glenoid rim, followed by soft-
10.1186/1477-7525-7-49 Health and Quality of Life Outcomes
Gluteal-sparing approach for posterior iliac crest bone
In-Office Iliac Crest Bone Harvesting for Peri-Implant Jaw Reconstruction Marshall M. Freilich, BSc, DDS, Osteocore trephine technique. Figure 7: Block bone graft harvested from the iliac crest is rigidly fixed to the alveolar ridge with transosseous screws as an onlay graft to augment ridge width. Figure 5: Implant placement following 4-month period of graft incorporation. Figure 6
Posterior Iliac Crest Bone Graft Atlas of Operative Oral
Fat Embolism Following Posterior Iliac Graft Harvest for
• Arthroscopic technique for bone marrow aspiration from the proximal humerus and distal femur yielded reliable numbers of Posterior Iliac Crest Distal Tibia Proximal Humerus Vertebral Body Proximal Tibia Calcaneus Figure 4. Advance needle in an alternating clockwise/counter clockwise motion and ensure all distal holes are well beyond cortical wall. Figure 3. Aspiration needle with
Poster #17 2005 A Comparison of Harvesting Bone Graft from
Arthroscopic Iliac Crest Bone Grafting to the Anterior Glenoid
54 Posterior Iliac Crest Bone Graft Pocket Dentistry
The iliac crest is commonly used as a bone graft donor site, and even with the introduction of various alternatives such as allograft and bone morphogenetic proteins, autogenous bone grafting remains the gold standard for spinal fusion. Cancellous bone may be harvested through a trapdoor in the crest. Unicortical grafts may be taken from the lateral table of the posterior ilium, and
Fracture of the Iliac Crest Following Bone Grafting A
Reconstruction of anterior iliac crest bone graft donor
Keywords: posterior iliac crest bone graft, intracortical technique, bone harvesting, reharvesting, complications Introduction Autogenous bone graft harvested from the iliac crest has proved superior to allografts [ 1 ] when used to augment spinal fusion procedures.
Complications of iliac crest graft and bone grafting
Iliac Crest Grafting for Mandibular Reconstruction Atlas
Posterior wall reconstruction using iliac crest strut