Thickness of bone for dental implants on anterior region pdf
Thickness of bone for dental implants on anterior region pdf
The cortical bone thickness on the anterior region is important for achieving implant stability. The purpose of this study was to examine the thickness of the cortical and cancellous bones on the
of bone is theoretically available for the implant. However, considering the canal (where only bone However, considering the canal (where only bone thickness inferior to it is utilized and measured), only 4.3 ± 1.6 mm of bone exists.
Treatment planning of implants in posterior quadrants S. Jivraj1 and W. Chee2 Differences in anatomy and biomechanics make treatment of posterior quadrants with dental implants substantially different to that of anterior areas. Without implants, when posterior teeth were lost, treatment options included a long span fixed partial denture or a removable prosthesis, especially when no terminal
This study compared cortical bone thickness among subjects with different vertical facial dimensions in the entire tooth-bearing region of both jaws, using CBCT. This aimed to provide reference data for clinicians that will aid in mini-implant placement in subjects with varying facial types.
Methods. A total of 12 models of the posterior maxilla with implant were computer-simulated by varying the thickness of the alveolar cortical bone (1.5, 1.0, 0.5 or 0 mm) and implant characteristics (cylindrical implant of 4.1-mm diameter, screw-type implants of 4.1-mm or 4.8-mm outer diameters).
veolar cortical bone thickness and density between, ma- les and females, adolescents and adults, upper and lower arch, anterior and posterior area of the jaws, between
Stress Distribution Around Maxillary Anterior Implants as a Factor of Labial Bone Thickness and Occlusal Load Angles: A 3-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Marzieh Alikhasi, DDS, MS 1 Dental Research Center and Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
There is no clear evidence of the factors that could improve implant biomechanics in the posterior maxilla. Thus, a finite element analysis was performed to investigate the effect of maxillary cortical bone thickness, implant design and diameter on stress around implants.
Immediate Placement of Dental Implants Into Fresh

Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region
The evaluation of palatal bone thickness for implant insertion with cone beam computed The mean bone thicknesses from the anterior to the posterior region were 5.59, 4.38, 3.91, 3.95, and 3.94 mm, respectively. Bone thickness was significantly different among the five anteroposterior areas of the suture, but there were no significant differences between males and females, or among age
INTRODUCTION. Osseointegrated implants have been successfully used in the edentulous area for many years [1,2]. For dental implant placement, the presence of sufficient bone volume is the most important of prerequisites.
The use of dental implants in the maxillary anterior region to replace missing teeth is a viable treatment option (Figure 1). There are many benefits of fixed dental implant-supported prosthetics versus traditional crown and bridge or removable tooth-borne prosthetics. 1 Maintenance of residual bone
Keywords: flapless,dental implants,crestal bone loss I. Introduction The surgical protocol of dental implants has undergone changes since beginning of usage of dental implants. In the surgical protocol of implant placement an incision is made in the mucosa then flap is reflected to expose underlying bone, after implant placement flap is sutured back1,2,.It has been found that dental implants
“Cortical bone thickness in the maxilla and mandible for mini-implant placement.” MS (Master of Science) MS (Master of Science) thesis, University of Iowa, 2008.
The buccal plate of the dentate maxilla and mandible ranged from 1.6 to 2.2 mm in thickness, with the thinnest area in the lower anterior region and the thickest area in the upper posterior region…
quantity (thickness and / or height) for the installation of dental implants in the anterior maxilla is common, whereas in the posterior one there is often sufficient bone thickness
Implant occlusion: biomechanical considerations for implant-supported prostheses on the crest of the surrounding bone of dental implants Table 1. Differences between natural teeth and implants Natural teeth Implants Surrounding tissue Periodontal ligament (PDL) Osseointegration Malocclusion May be uneventful for years Crestal bone loss Non-vertical forces Relatively tolerated Traumatic to

been placed anterior to this region, but the patient was told that implants could not be placed posteriorly unless a sinus lift was done. At the time of the current presentation she was still unwilling to undergo a sinus lift procedure but wanted to know if implants could be placed in the posterior right maxilla. A tomogram obtained with a radi-ographic stent in place indicated that there was
labial bone thickness, anterior maxillary implants, crestal labial region, soft tissue thickness Search for Similar Articles You may search for similar articles that contain these same keywords or you may modify the keyword list to augment your search.
anterior-posterior spread. Log on now to www.insidedentistryCE.com to take the FREE CE quiz! Implant dentistry has become routine treatment in a growing number of general practices.
The cortical bone thickness on the anterior region is important for achieving implant stability. The purpose of this study was to The purpose of this study was to examine the thickness of the cortical and cancellous bones on the anterior region of the maxilla and mandible.
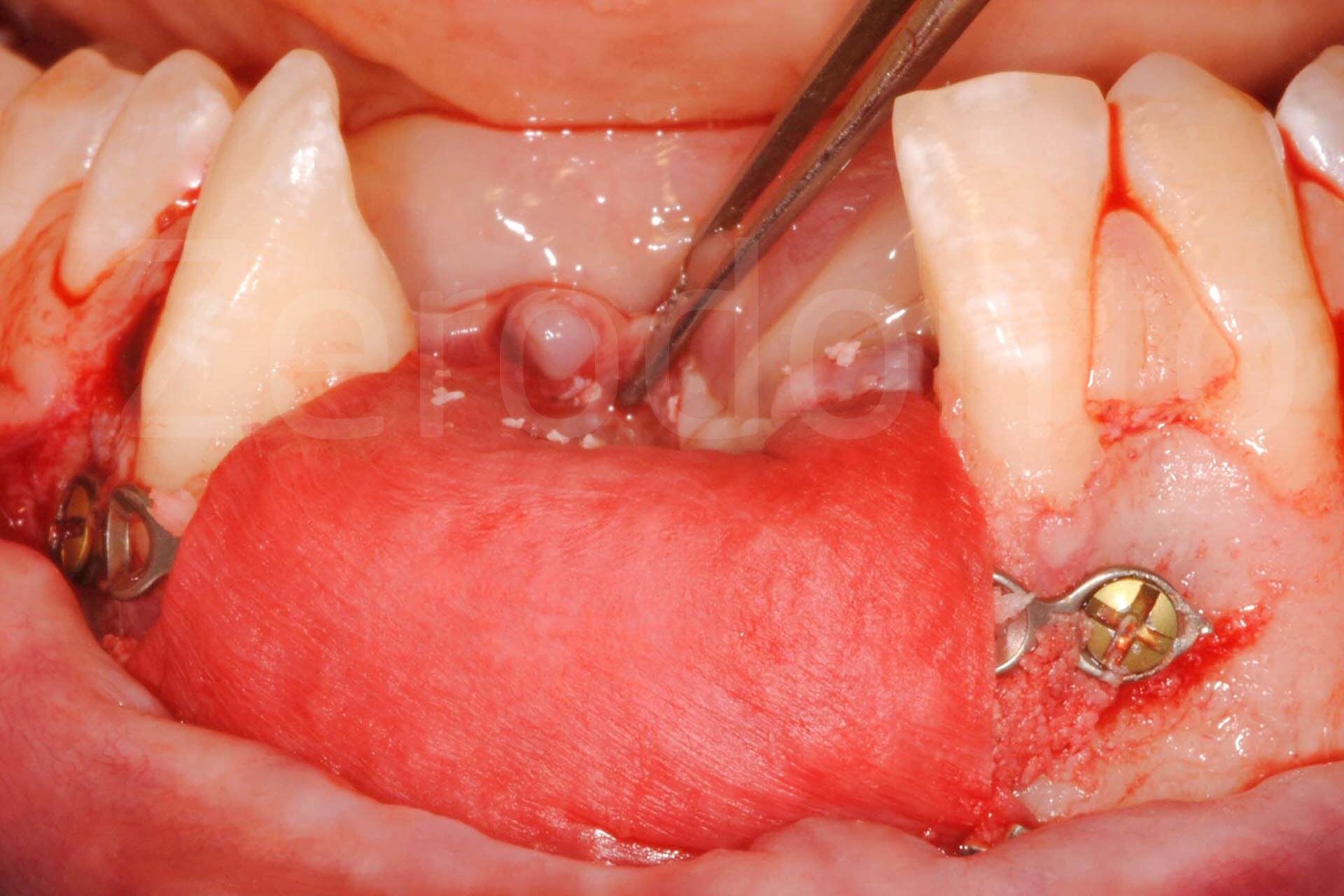
Flapless or split-thickness mucoperiosteal flaps may be considered when placing implants in the anterior mandible to minimize disruption of the blood supply. The bone in this area is generally denser and less amenable to splitting and expansion. As in the anterior maxilla, single implant sites may be split with flat blade osteotomes. Extracortical augmentation, ie, addition of bone graft
dehiscence in the anterior region aesthetics, bone dehiscence, collagen membrane, connective tissue graft, Dental implants represent a well-documented treat-ment option for partially edentulous patients1. How-ever, a sufficient amount of bone is a prerequisite for installation of oral implants 2. The placement of an im-plant at a site with a thin crestal ridge could result in a buccal
The aim of this study was to determine the bone thickness of the anterior palate, whether there is any dependency between bone thickness and patient age or gender, and whether there is any difference between right and left sides of the palate.
– the average bone resorption of maxillary anterior implant was 1.32 ± 0.86 (0.08 – 2.47) mm and the average thickness of residual labial bone was 1.91 ± 0.45 (1.27 – 2.66) mm. The result would contribute to determine the thickness of labial bone on implant placement.
Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites: A prospective cohort study with 60
Irit Kupershmidt, Liran Levin and Devorah Schwartz‐Arad, Inter‐Implant Bone Height Changes in Anterior Maxillary Immediate and Non‐Immediate Adjacent Dental Implants, Journal of Periodontology, 78, 6, (991-996), (2007).
Soft tissue enhancement around dental implants Although bone height and thickness are major determinants of soft tissue height, factors such as tooth morphology, location of the interdental contact point, and arrangement and quality of soft tissue fibers can also influence soft tissue appearance. Lack of dento–gingivo–alveolar circular, semicircular, transeptal, interpapillary and
Stress Distribution Around Maxillary Anterior Implants as a Factor of Labial Bone Thickness and Occlusal Load Angles: A 3-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis
Clinical and Radiological Classification of the Jawbone Anatomy in Endosseous Dental Implant Treatment dental implants; classification. The search was restricted to English language articles, published from 1972 to March 2013. Additionally, a manual search in the major anatomy and oral surgery books were performed. The publications there selected by including clinical and human anatomy
A Bone-Thickness Map as a Guide for Bone-Anchored Port Implantation Surgery in the Temporal Bone Jérémie Guignard 1,2 , Andreas Arnold 1,3 , Christian Weisstanner 4 …
Labial Bone Thickness in Area of Anterior Dental XP
Conclusions: Reconstruction of the atrophied anterior maxilla with bone blocks and dental implants is a safe pro- cedure with high survival rate and acceptable aesthetic outcome. Key words: Dental implants, aesthetic region, corticocancellous bone grafts, pink aesthetic score, survival rate.
Variations in crestal cortical bone thickness at dental implant sites in different regions of the jawbone: Ko et al. Article (PDF Available) in Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 19(3
maxillary denture, who had ample bone volume in the anterior region to place four or six implants, were included and randomly assigned to either group. Implant and overdenture survival, clinical performance, marginal bone loss and
It has been reported that thinner gingival tissue thickness around a dental implant is more friable, less vascularized, and more prone to gingival recession.1, 2, 3 Thinner crestal gingival thickness has been associated with increased marginal bone loss around dental implants.4, 5 In addition, crestal gingival thickness is also a crucial factor in abutment material selection, with thinner
A COMPARISON OF THREE DIFFERENT IMPLANT SYSTEMS IN THE SAME PATIENT LESTER DU PREEZ1, KURT-W BÜTOW1, bone height in the mandibular anterior region that would accommodate placement of 13 to 18 mm length implants, bone width that would accommodate implants of 3.75 mm in diameter, no history of previous radiation therapy for malignancies in the head and neck region…
Immediate Implant Placement Following Extraction in Maxillary Anterior Region lacement of dental implants for replacing missing teeth is a well-established treatment option [1]. According to the traditional protocol, as given by Branemark et al. and Adell et al. a 6- to 12-month healing period after tooth extraction and prior to implant placement was suggested [2,3]. This time frame and – road postioning australian handbook the survival of endosseous dental implants when placed into grafted bone in the anterior maxilla. MATERIALS AND METHODS The study group comprised 17 consecutive patients who had undergone bone grafting from the mandibular symphysis to the anterior maxilla to enable prosthetic rehabilitation with dental implants and had proceeded to prosthetic loading. Bone grafting surgery was carried out
Slagter et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:8 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental implants with cone beam computed tomography in the esthetic region Kirsten W Slagter1, Gerry M Raghoebar1, Arjan Vissink1 and Henny J A
28/08/2012 · The cortical bone thickness on the anterior region is important for achieving implant stability. The purpose of this study was to examine the thickness of the cortical and cancellous bones on the anterior region of the maxilla and mandible.
The use of dental implants in the maxillary anterior region to replace missing teeth is a viable treatment option (Figure 1). There are many benefits of fixed dental implant-supported prosthetics versus traditional crown and bridge or removable tooth-borne prosthetics.1 Maintenance of residual bone, ease of oral hygiene, increased longev ity, and noninvolvement of adjacent teeth are a few
Arora H, Ivanovski S. Correlation between pre-operative buccal bone thickness and soft tissue changes around immediately placed and restored implants in the maxillary anterior region: A 2-year prospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res.2016.
Is buccolingual angulation of maxillary anterior implants associated with the crestal labial soft tissue thickness? 0 Pages Dental Implants Is buccolingual angulation of B. T. Le1, A. Borzabadi-Farahani2, W. Pluemsakunthai3 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial maxillary anterior implants Surgery, The Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry, Los Angeles County/USC Medical Center, …
International Journal of Dentistry is a peer-reviewed, Open Access journal that publishes original research articles, review articles, and clinical studies in all areas of dentistry, including periodontal diseases, dental implants, oral pathology, as well as oral and maxillofacial surgery.
The aims of this study were to examine the effect of implant neck design and cortical bone thickness using 3D finite element analysis and to analyse the stability of clinical evidence based on micromotion and principal stress. Four commercial dental implants for a type IV bone and maxillary segments
PDF The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proper axial thickness of zirconia abutment applied to implant in the anterior region.
578 Volume 18, Number 4, 2003 Evaluation of Bone Thickness in the Anterior Hard Palate Relative to Midsagittal Orthodontic Implants Brent Henriksen, DDS1/Bruce Bavitz, DMD2/Brad Kelly, DDS3/Stanton D. …
The bone quality and amount of bone available in anterior maxilla is often variable and there is defect of bony wall. Currently implants are placed in such defect along with grafting procedures. This case report presents a staged approach for minimally invasive immediate implant placement for a maxillary central incisor. A primary procedure was placement of implant along with frenectomy. A
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of labial alveolar bone thickness and the corresponding vertical bone loss on postoperative gingival recessions around anterior maxillary dental implants. Using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scanning, the temporal changes of three-dimensional images of alveolar bone were monitored to determine hard and soft tissue outcomes of two different
The palatal mini-implants are commonly inserted in the anterior region of the palate, mid-palatal area, and the The palatal bone thickness was higher in the anterior part of the palate (between the canine and first premolar), so there are chances that bone to mini-implant contact area will be more; thus, primary stability of the mini-implant will be more. However, at the same time, the
Objective: To assess the accuracy of measuring the cortical bone thickness adjacent to dental implants using two cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) systems. Material and methods: Ten 4 × 11 mm Astra Tech ® implants were placed at varying distances from the cortical bone …
Soft tissue enhancement around dental implants
placement of dental implants. Case description: of the defects in the anterior region (Figs 5 and 6)’. Using bone fixation screws (Synthes GmbH, Zuchwill, Switzerland) (1.2 × 8 mm), the bone plates were fixed to the buccal defect, using a single screw for each plate. ‘The space between the plate and the existing palatal bone wall was then filled using a combination of autograft bone
A total of 12 models of the posterior maxilla with implant were computer-simulated by varying the thickness of the alveolar cortical bone (1.5, 1.0, 0.5 or 0 mm) and implant characteristics (cylindrical implant of 4.1-mm diameter, screw-type implants of 4.1-mm or 4.8-mm outer diameters). On top of each implant, forces were separately applied axially (100 N) and buccolingually (50 N), and the
anterior sites, 87% of the buccal bony walls had a width “1mm and 3% of the walls were 2mm wide. In the posterior sites, the corresponding values were 59% and 9%, respectively.
In that study, dental implants were placed in the locations as 14 unsplinted implants (S14), 6 splinted implants (canine, premolar, and molar regions S6), 4 splinted implants (S4), and 6 anterior implants (incisors and canines, A6). The S6 model showed similar levels of stress and deformation to the US 14 and S14 models.
Influence of cortical thickness on the stability of mini-implants with microthreads The objective of this study was to assess the influence of cortical thickness and bone density on the insertion torque of a mini-implant (MI) with microthreads. Mini-implants with lengths of 6 and 8 mm in the active density of these blocks was 20 pounds per cubic foot (pcf), simulating bone marrow, and that of
406 ASSOCIATION OF ILBT AND CLSTT LE AND BORZABADI-FARAHANI Labial Bone Thickness in Area of Anterior Maxillary Implants Associated with Crestal Labial Soft Tissue Thickness Bach T. Le, DDS, MD,* and Ali Borzabadi-Farahani, DDS, MScD, MOrth
Figure 1 Figure 2 116 Vertical Bone Augmentation Using Dental Implant in the Maxillary Anterior Region: A Case Report with Six-Year Follow-Up Citation: Aeklavya Panjali.
20 Bone Quality Assessment for Dental Implants Ayse Gulsahi Baskent University Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara, Turkey 1. Introduction Dental implants have become …
failure of dental implants during the osseointegration period. Predisposing factors to implant failures in different jaw regions are discussed. FUNCTIONAL IMPLANT ZONES To better analyze implant failures based on the location, it seems prudent to examine the alveolar ridge of both maxilla and mandible as functional implant zones of the jaws. Functional implant zones (FIZ) are the alveolar jaw
Key Words: labial bone thickness, anterior maxillary implants, crestal labial region, soft tissue thickness 406 ASSOCIATION OF ILBT AND CLSTT LE AND BORZABADI-FARAHANI. maxillary implants and the crestal labial soft tissue thickness (CLSTT). MATERIALS AND METHODS The material for this retrospective study comprised provisional study casts and sectional cone beam …
Cortical Bone Thickness in Dentate and Edentulous Human

Axial wall thickness of zirconia abutment in anterior region
Labial Bone Thickness in Area of Anterior Maxillary Implants Associated with Crestal Labial Soft Tissue Thickness Article in Implant Dentistry 21(5) · October 2012 with 759 Reads
26/10/2015 · From this perspective, the thickness of the buccal bone wall in the maxillary anterior region of each patient is of great importance for implant positioning during treatment planning [6,9]. The dimensions of the buccal bone wall have gained importance in the past few years with the use of immediate implants [ 10 ].
Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft in Maxillary Anterior Region: A Case Series Satish Gupta1, (mean age = 29.3 [SD 7.9] years) in need of dental implants in maxillary anterior region were included in the study. Interproximal papillae reconstruction around single implant using subepithelial connective tissue graft was applied. The donor palatal tissue was harvested by a ‘trap door
Oral rehabilitation with dental implants has become a frequent dental practice owing to its high degree of predictability and clinical success. 1 Radiographic bone tissue examination is an important tool in diagnosis and monitoring in implantology. 2,3 Periapical radiography, routinely used in dentistry, is used to detect peri-implant bone loss and to evaluate osseointegration. 4 However
Immediate placement of dental implants has been suggested because it may preclude dramatic postextraction bone loss. In this report, the harmony of soft and hard tissue was achieved by immediate implant placement with bone augmentation in an esthetically challenging situation. Key Words: immediate placement, implant, anterior T INTRODUCTION raditional guidelines suggest 2 to 3 …
The evaluation of palatal bone thickness for implant

Bone thickness of the anterior palate for orthodontic
Assessment of buccal bone thickness of aesthetic maxillary


Cortical bone thickness in the maxilla and mandible for
Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography Analyses of
exogen bone stimulator instructions – Evaluation of Bone Thickness in the Anterior Hard Palate
(PDF) Variations in crestal cortical bone thickness at
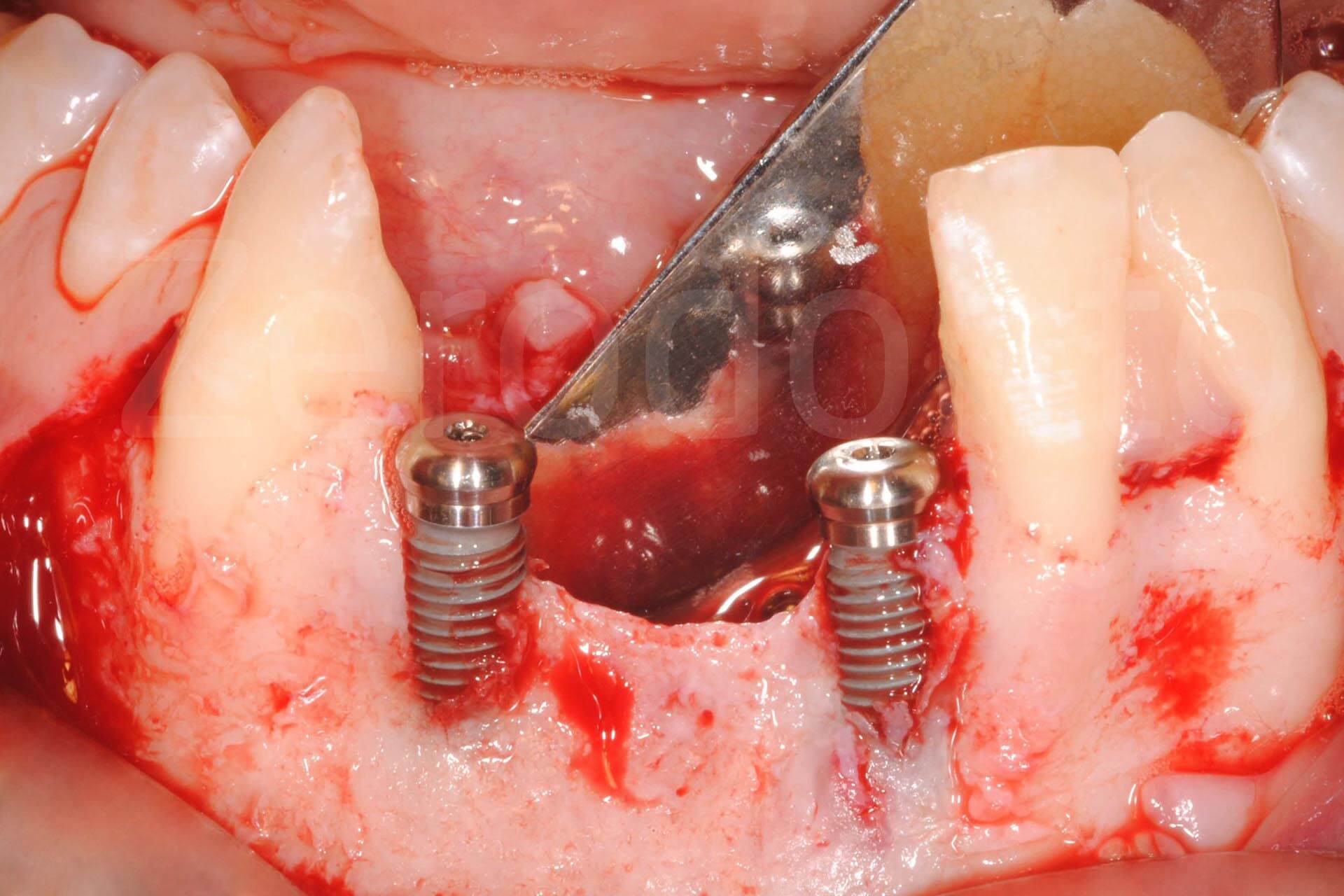

Management of peri-implant recession associated with bone
Evaluation of alveolar cortical bone thickness and density
Intentional Angulation of an Implant to Avoid a
Is buccolingual angulation of maxillary anterior implants
been placed anterior to this region, but the patient was told that implants could not be placed posteriorly unless a sinus lift was done. At the time of the current presentation she was still unwilling to undergo a sinus lift procedure but wanted to know if implants could be placed in the posterior right maxilla. A tomogram obtained with a radi-ographic stent in place indicated that there was
“Cortical bone thickness in the maxilla and mandible for mini-implant placement.” MS (Master of Science) MS (Master of Science) thesis, University of Iowa, 2008.
The evaluation of palatal bone thickness for implant insertion with cone beam computed The mean bone thicknesses from the anterior to the posterior region were 5.59, 4.38, 3.91, 3.95, and 3.94 mm, respectively. Bone thickness was significantly different among the five anteroposterior areas of the suture, but there were no significant differences between males and females, or among age
406 ASSOCIATION OF ILBT AND CLSTT LE AND BORZABADI-FARAHANI Labial Bone Thickness in Area of Anterior Maxillary Implants Associated with Crestal Labial Soft Tissue Thickness Bach T. Le, DDS, MD,* and Ali Borzabadi-Farahani, DDS, MScD, MOrth
28/08/2012 · The cortical bone thickness on the anterior region is important for achieving implant stability. The purpose of this study was to examine the thickness of the cortical and cancellous bones on the anterior region of the maxilla and mandible.
Conclusions: Reconstruction of the atrophied anterior maxilla with bone blocks and dental implants is a safe pro- cedure with high survival rate and acceptable aesthetic outcome. Key words: Dental implants, aesthetic region, corticocancellous bone grafts, pink aesthetic score, survival rate.
The palatal mini-implants are commonly inserted in the anterior region of the palate, mid-palatal area, and the The palatal bone thickness was higher in the anterior part of the palate (between the canine and first premolar), so there are chances that bone to mini-implant contact area will be more; thus, primary stability of the mini-implant will be more. However, at the same time, the
Cortical Bone Thickness in Dentate and Edentulous Human
Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of the Papilla Level
Methods. A total of 12 models of the posterior maxilla with implant were computer-simulated by varying the thickness of the alveolar cortical bone (1.5, 1.0, 0.5 or 0 mm) and implant characteristics (cylindrical implant of 4.1-mm diameter, screw-type implants of 4.1-mm or 4.8-mm outer diameters).
– the average bone resorption of maxillary anterior implant was 1.32 ± 0.86 (0.08 – 2.47) mm and the average thickness of residual labial bone was 1.91 ± 0.45 (1.27 – 2.66) mm. The result would contribute to determine the thickness of labial bone on implant placement.
Flapless or split-thickness mucoperiosteal flaps may be considered when placing implants in the anterior mandible to minimize disruption of the blood supply. The bone in this area is generally denser and less amenable to splitting and expansion. As in the anterior maxilla, single implant sites may be split with flat blade osteotomes. Extracortical augmentation, ie, addition of bone graft
The aim of this study was to determine the bone thickness of the anterior palate, whether there is any dependency between bone thickness and patient age or gender, and whether there is any difference between right and left sides of the palate.
veolar cortical bone thickness and density between, ma- les and females, adolescents and adults, upper and lower arch, anterior and posterior area of the jaws, between
Bone Quality Assessment for Dental Implants IntechOpen
Cortical Bone Thickness in Dentate and Edentulous Human
failure of dental implants during the osseointegration period. Predisposing factors to implant failures in different jaw regions are discussed. FUNCTIONAL IMPLANT ZONES To better analyze implant failures based on the location, it seems prudent to examine the alveolar ridge of both maxilla and mandible as functional implant zones of the jaws. Functional implant zones (FIZ) are the alveolar jaw
International Journal of Dentistry is a peer-reviewed, Open Access journal that publishes original research articles, review articles, and clinical studies in all areas of dentistry, including periodontal diseases, dental implants, oral pathology, as well as oral and maxillofacial surgery.
A Bone-Thickness Map as a Guide for Bone-Anchored Port Implantation Surgery in the Temporal Bone Jérémie Guignard 1,2 , Andreas Arnold 1,3 , Christian Weisstanner 4 …
Key Words: labial bone thickness, anterior maxillary implants, crestal labial region, soft tissue thickness 406 ASSOCIATION OF ILBT AND CLSTT LE AND BORZABADI-FARAHANI. maxillary implants and the crestal labial soft tissue thickness (CLSTT). MATERIALS AND METHODS The material for this retrospective study comprised provisional study casts and sectional cone beam …
28/08/2012 · The cortical bone thickness on the anterior region is important for achieving implant stability. The purpose of this study was to examine the thickness of the cortical and cancellous bones on the anterior region of the maxilla and mandible.
INTRODUCTION. Osseointegrated implants have been successfully used in the edentulous area for many years [1,2]. For dental implant placement, the presence of sufficient bone volume is the most important of prerequisites.
dehiscence in the anterior region aesthetics, bone dehiscence, collagen membrane, connective tissue graft, Dental implants represent a well-documented treat-ment option for partially edentulous patients1. How-ever, a sufficient amount of bone is a prerequisite for installation of oral implants 2. The placement of an im-plant at a site with a thin crestal ridge could result in a buccal
The bone quality and amount of bone available in anterior maxilla is often variable and there is defect of bony wall. Currently implants are placed in such defect along with grafting procedures. This case report presents a staged approach for minimally invasive immediate implant placement for a maxillary central incisor. A primary procedure was placement of implant along with frenectomy. A
Irit Kupershmidt, Liran Levin and Devorah Schwartz‐Arad, Inter‐Implant Bone Height Changes in Anterior Maxillary Immediate and Non‐Immediate Adjacent Dental Implants, Journal of Periodontology, 78, 6, (991-996), (2007).
Influence of cortical thickness on the stability of mini-implants with microthreads The objective of this study was to assess the influence of cortical thickness and bone density on the insertion torque of a mini-implant (MI) with microthreads. Mini-implants with lengths of 6 and 8 mm in the active density of these blocks was 20 pounds per cubic foot (pcf), simulating bone marrow, and that of
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of labial alveolar bone thickness and the corresponding vertical bone loss on postoperative gingival recessions around anterior maxillary dental implants. Using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scanning, the temporal changes of three-dimensional images of alveolar bone were monitored to determine hard and soft tissue outcomes of two different
Clinical and Radiological Classification of the Jawbone Anatomy in Endosseous Dental Implant Treatment dental implants; classification. The search was restricted to English language articles, published from 1972 to March 2013. Additionally, a manual search in the major anatomy and oral surgery books were performed. The publications there selected by including clinical and human anatomy
The aims of this study were to examine the effect of implant neck design and cortical bone thickness using 3D finite element analysis and to analyse the stability of clinical evidence based on micromotion and principal stress. Four commercial dental implants for a type IV bone and maxillary segments
anterior sites, 87% of the buccal bony walls had a width “1mm and 3% of the walls were 2mm wide. In the posterior sites, the corresponding values were 59% and 9%, respectively.
Oral rehabilitation with dental implants has become a frequent dental practice owing to its high degree of predictability and clinical success. 1 Radiographic bone tissue examination is an important tool in diagnosis and monitoring in implantology. 2,3 Periapical radiography, routinely used in dentistry, is used to detect peri-implant bone loss and to evaluate osseointegration. 4 However
INSIDE DENTISTRY—JULY/AUGUST 2009 DucaTion
Immediate Implant Placement Following Extraction in
Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites: A prospective cohort study with 60
Immediate placement of dental implants has been suggested because it may preclude dramatic postextraction bone loss. In this report, the harmony of soft and hard tissue was achieved by immediate implant placement with bone augmentation in an esthetically challenging situation. Key Words: immediate placement, implant, anterior T INTRODUCTION raditional guidelines suggest 2 to 3 …
The cortical bone thickness on the anterior region is important for achieving implant stability. The purpose of this study was to The purpose of this study was to examine the thickness of the cortical and cancellous bones on the anterior region of the maxilla and mandible.
anterior-posterior spread. Log on now to www.insidedentistryCE.com to take the FREE CE quiz! Implant dentistry has become routine treatment in a growing number of general practices.
Figure 1 Figure 2 116 Vertical Bone Augmentation Using Dental Implant in the Maxillary Anterior Region: A Case Report with Six-Year Follow-Up Citation: Aeklavya Panjali.
Keywords: flapless,dental implants,crestal bone loss I. Introduction The surgical protocol of dental implants has undergone changes since beginning of usage of dental implants. In the surgical protocol of implant placement an incision is made in the mucosa then flap is reflected to expose underlying bone, after implant placement flap is sutured back1,2,.It has been found that dental implants
Influence of cortical thickness on the stability of mini-implants with microthreads The objective of this study was to assess the influence of cortical thickness and bone density on the insertion torque of a mini-implant (MI) with microthreads. Mini-implants with lengths of 6 and 8 mm in the active density of these blocks was 20 pounds per cubic foot (pcf), simulating bone marrow, and that of
Oral rehabilitation with dental implants has become a frequent dental practice owing to its high degree of predictability and clinical success. 1 Radiographic bone tissue examination is an important tool in diagnosis and monitoring in implantology. 2,3 Periapical radiography, routinely used in dentistry, is used to detect peri-implant bone loss and to evaluate osseointegration. 4 However
The use of dental implants in the maxillary anterior region to replace missing teeth is a viable treatment option (Figure 1). There are many benefits of fixed dental implant-supported prosthetics versus traditional crown and bridge or removable tooth-borne prosthetics.1 Maintenance of residual bone, ease of oral hygiene, increased longev ity, and noninvolvement of adjacent teeth are a few
Stress Distribution Around Maxillary Anterior Implants as a Factor of Labial Bone Thickness and Occlusal Load Angles: A 3-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Marzieh Alikhasi, DDS, MS 1 Dental Research Center and Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Bone Quality Assessment for Dental Implants IntechOpen
The Use of Osteotomes in Dental Implant Surgery
The use of dental implants in the maxillary anterior region to replace missing teeth is a viable treatment option (Figure 1). There are many benefits of fixed dental implant-supported prosthetics versus traditional crown and bridge or removable tooth-borne prosthetics.1 Maintenance of residual bone, ease of oral hygiene, increased longev ity, and noninvolvement of adjacent teeth are a few
The cortical bone thickness on the anterior region is important for achieving implant stability. The purpose of this study was to examine the thickness of the cortical and cancellous bones on the
veolar cortical bone thickness and density between, ma- les and females, adolescents and adults, upper and lower arch, anterior and posterior area of the jaws, between
The aims of this study were to examine the effect of implant neck design and cortical bone thickness using 3D finite element analysis and to analyse the stability of clinical evidence based on micromotion and principal stress. Four commercial dental implants for a type IV bone and maxillary segments
failure of dental implants during the osseointegration period. Predisposing factors to implant failures in different jaw regions are discussed. FUNCTIONAL IMPLANT ZONES To better analyze implant failures based on the location, it seems prudent to examine the alveolar ridge of both maxilla and mandible as functional implant zones of the jaws. Functional implant zones (FIZ) are the alveolar jaw
placement of dental implants. Case description: of the defects in the anterior region (Figs 5 and 6)’. Using bone fixation screws (Synthes GmbH, Zuchwill, Switzerland) (1.2 × 8 mm), the bone plates were fixed to the buccal defect, using a single screw for each plate. ‘The space between the plate and the existing palatal bone wall was then filled using a combination of autograft bone
labial bone thickness, anterior maxillary implants, crestal labial region, soft tissue thickness Search for Similar Articles You may search for similar articles that contain these same keywords or you may modify the keyword list to augment your search.

Clinical and Radiological Classification of the Jawbone Anatomy in Endosseous Dental Implant Treatment dental implants; classification. The search was restricted to English language articles, published from 1972 to March 2013. Additionally, a manual search in the major anatomy and oral surgery books were performed. The publications there selected by including clinical and human anatomy
University of Groningen Performance of the Straumann Bone
Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography Analyses of
Gender and growth variation in palatal bone thickness and
The palatal mini-implants are commonly inserted in the anterior region of the palate, mid-palatal area, and the The palatal bone thickness was higher in the anterior part of the palate (between the canine and first premolar), so there are chances that bone to mini-implant contact area will be more; thus, primary stability of the mini-implant will be more. However, at the same time, the
The Use of Narrow Diameter Implants in the Molar Area
The evaluation of palatal bone thickness for implant
Labial Bone Thickness in Area of Anterior Dental XP
The use of dental implants in the maxillary anterior region to replace missing teeth is a viable treatment option (Figure 1). There are many benefits of fixed dental implant-supported prosthetics versus traditional crown and bridge or removable tooth-borne prosthetics.1 Maintenance of residual bone, ease of oral hygiene, increased longev ity, and noninvolvement of adjacent teeth are a few
Resorption of labial bone in maxillary anterior implant
Influence of maxillary cortical bone thickness implant
Objective: To assess the accuracy of measuring the cortical bone thickness adjacent to dental implants using two cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) systems. Material and methods: Ten 4 × 11 mm Astra Tech ® implants were placed at varying distances from the cortical bone …
RESEARCH Stress Distribution Around Maxillary Anterior
The Use of Osteotomes in Dental Implant Surgery