Stages of bone formation pdf
Stages of bone formation pdf
Gynecomastia Glandular development due to changes in hormone levels during puberty (estrogenic-androgenic balance) 1/3 of healthy guys Usually resolves in 3-24 months without intervention.
Copper aids in the formation of bone collagen and is important to the healing process. The body’s demand for both copper and zinc rises according to the severity of the trauma. 8
Fracture healing involves a complex and sequential set of events to restore injured bone to pre-fracture condition stem cells are crucial to the fracture repair process the …
Early Stages of Bone Fracture Healing. 3 formation and (ii)to ascertain their dependence on the kinetics of relevant un-derlying mechanisms as platelet activation, fibrin polymerization and fibrin
collagen) and bone formation (due to osteoblasts). Normally, these processes are balanced, resulting in 10 % Normally, these processes are balanced, resulting in 10 % replacement of the skeleton, each year.
Stages of Endochondral Ossification Figure 6.8 Formation of bone collar around hyaline cartilage model. Hyaline cartilage Cavitation of the hyaline carti-lage within the cartilage model. Invasion of internal cavities by the periosteal bud and spongy bone formation. Formation of the medullary cavity as ossification continues; appearance of sec-ondary ossification centers in the epiphy-ses in
This work is concerned with the sequence of events taking place during the first stages of bone fracture healing, from bone breakup until the formation of early fibrous callus (EFC).
Intramembranous bone formation is a more direct process, in which osteoprogenitor cells form bone directly. Cranial bones are formed by this process during development. Wound healing in bone may proceed by either process, depending on local environmental factors that include how much the ends of the bone can move relative to each other, with motion favoring the endochondral process
Endochondral ossification involves the formation of cartilage tissue from aggregated mesenchymal cells, and the subsequent replacement of cartilage tissue by bone (Horton 1990). The process of endochondral ossification can be divided into five stages ( Figure 14.13 ).
Figure 2. Stages in Fracture Repair. The healing of a bone fracture follows a series of progressive steps: (a) A fracture hematoma forms. (b) Internal and external calli form.
Low protein intake lowers both the production and action of a growth factor called IGF-1, which enhances bone formation. In addition, this growth factor stimulates the intestinal absorption of the bone mineral elements, calcium and phosphate, via an increase in the renal production of calcitriol, the hormonal form of …
Fracture healing SlideShare

FACIAL AND PALATAL DEVELOPMENT Columbia University
The proposed functions for osteocalcin in later stages of bone formation and remodeling have been extensively reviewed [111–113]. During bone development, osteocalcin production is very low and does not reach maximal levels until late stages of mineralization [114,115] .
INTRODUCTION
Fracture is a break in the structural continuity of bone or periosteum.
The healing of fracture is in many ways similiar to the healing in soft tissue wounds except that the end result is mineralised mesenchymal tissue i.e. BONE.
Fracture healing starts as soon as bone breaks and continues modelling for many years.
54 F Shapiro Bone development and fracture repair stages of bone formation, in an environment where no pre-existing bone matrix is present, undifferentiated
Two Processes of Bone Formation A fetal skeleton has 275 bones, while a adult skeleton has only 206 due to bone fusion. We obviously have a lot of growing to do after we’re born.
Chapter 1. Bone Embryology Bjorn R. Olsen Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Department of Developmental Biology, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts INTRODUCTION The cells that make up the vertebrate skeleton are derived from three lineages. Neural crest cells give rise to the branchial arch derivatives of the craniofacial skeleton, paraxial mesoderm
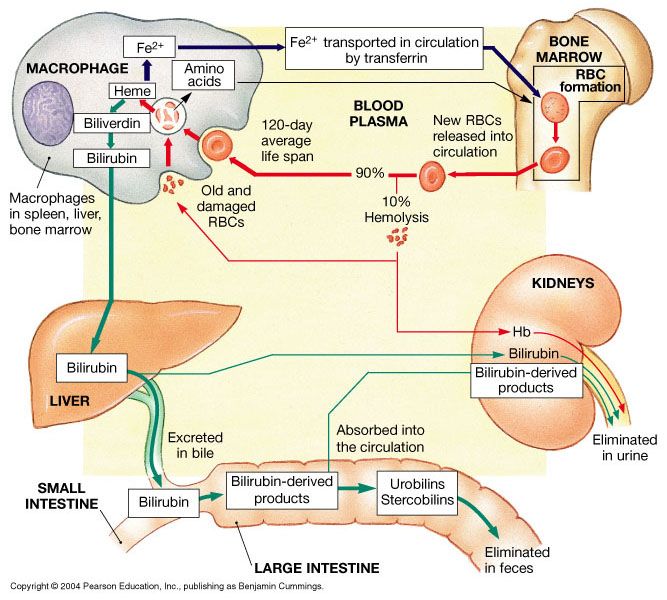
During intrauterine development, the early stages of life, erythrocytes are produced first by the yolk sac and then by the developing spleen during the third month of gestation, until the bone marrow is formed in the seventh month and takes over erythrocyte production exclusively.
I simplified the steps and left out some details to remember the order that bone formation occurs. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.

stages of bone formation 1. Growth andGrowth and Development of BoneDevelopment of Bone 2. IntroductionIntroduction Bone is a relatively hard and lightweightBone is a relatively hard and lightweight composite material, formed mostly ofcomposite material, formed mostly of calcium phosphatecalcium phosphate Bone
Bone Formation. The skeleton of the fetus begins developing bones about 13 weeks following conception. The bones gradually become harder and muscle tissue begins to develop.
Platelets are formed from cells in the bone marrow called as 50% of marrow megakaryocytes and are wholly engaged in platelet formation. Fig. 11.1: A stage IV megakaryocyte in the bone marrow Platelets are formed by fragmentation of the cytoplasm of megakaryocyte. It has been shown that each megakaryocyte can give rise to 1000 to 5000 platelets. Each day an adult human produces 1×1011
When we talk about endochondral ossification we are talking about the development of long bones from a hyalin cartilage model. Bone Collar Formation The primary ossification center develops in the center of the bone, and is the source of bone development.
The stages of bone healing parallel the early stages of bone development. The bone healing process is greatly influenced by a variety of systemic and local factors. A thorough understanding of
Subperiosteal new bone formation begins. 3. Hard Callus: fracture late in this stage. Subperiosteal new bone can clearly be seen. is is the early formation of callus. Stage 3 is clearly evident on x-rays and the 9 month x-ray demonstrates this. ere is copious callus formation seen around the fracture site. e remodelling of Stage 4 is seen to occur over many years but there is usually
However, in early stages of bone formation, histomorphometric analysis showed no statistical differences between groups. This may be explained by the necessity of reabsorption of the graft particles before the new bone matrix is deposited without any increase of bone formation velocity. Also, there is a smaller area for new bone formation, since the graft occupies part of the defect space. In
Microarray analysis of gene expression was performed in the healing femur fractures of 13-week-old male rats during the inflammatory stage of repair, at 3 days post-fracture, and the endochondral bone formation stage of repair, at 11 days post-fracture.
The formation of bone during the fetal stage of development occurs by two processes: intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. Secondary ossification occurs after birth and forms the epiphyses of long bones and the extremities of irregular and flat bones.
Types of bone formation. Bone is formed in the embryo in two general ways. For most bones the general shape is first laid down as a cartilage model, which is then progressively replaced by bone (endochondral bone formation).
intramembrane ossification is formation of what type of bone tissue. spongy bone tissue. Endochondral ossification is the formation of which bones. diaphysis of long bones. purpose of compact bone . provide strength to bone. purpose of spongy bone. make the bone lighter in weight. bone forms within hyaline cartilage. endochondral ossification. Endochondral ossification – 1st stage. …
11-4 Fig. 11-2. The facial region of a 4-week-old human embryo, A, and of a young child, B, are shown, seen from front. The lightly stippled frontonasal process in A, will give rise to forehead, nose, and midsection of upper lip, similarly stippled in B.
The stages of endochondral bone formation include hematoma formation, inflammation, angiogenesis, cartilage formation, cartilage calcification, cartilage removal, bone formation, and finally bone remodeling. The external soft tissues and the periosteum of the fracture region supply the bridging or soft callus that stabilizes the fracture fragments[18]. In the remodeling phase, the young woven
Physiology and Pathophysiology of Bone Remodeling Lawrence G. Raisz The skeleton is a metabolically active organ that under-goes continuous remodeling throughout life.
Bone Growth and Remodeling University of Washington
Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an increased risk of fractures of the hip, spine, and wrist.
Fracture healing in children follows the same stages as that of adults but occurs at a much faster rate. Fractures heal by forming callus, which follows three overlapping phases: …
There are three primary stages of bone healing: 1. the early inflammatory stage 2. the repair stage 3. the late remodelling stage These stages are distinct, but there is overlap. 1. Inflammatory Stage – a hematoma (localized blood collection) forms within the fracture site during the first few hours and days. Inflammatory cells infiltrate the bone, which results in the formation of granulation
The objective of this thesis was to investigate the early stages of bone formation, which are accepted to be critical in the long-term success rate of dental implants, in hyperglycemic animal models compared to control groups using various microscopy techniques.
Fracture healing occurs naturally after traumatic bony disruption. This process begins with haemorrhage and progresses through three stages: inflammatory reparative remodelling This process can be supported by various treatment options with i…
TIMING AND RATE OF SKELETAL MATURATION IN HORSES, With Comments on Starting Young Horses and the State of the Industry ©2008 By Deb Bennett, Ph.D.
Primary bone formation as it occurs under rigid fixation in areas in which small gaps are present is called “gap healing.” Its first stage is characterized by the filling of the fracture gap by primary bone formation. Primary bone formation means that neither connective tissue nor fibrocartilage (as previously described) has been present prior to new bone being laid down. The pattern of the – road users handbook victoria 3 9 Successive stages of B cell development can be distinguished by correlated expression of various cell surface markers Randy Hardy’s scheme for fractionating bone marrow B cells.
bone defects. The general and local factors that are involved in such deficient The general and local factors that are involved in such deficient healing cases are detailed, in …
Bone regeneration is a complex, well-orchestrated physiological process of bone formation, which can be seen during normal fracture healing, and is involved in continuous remodelling throughout adult life.
Bone Development & Growth. The terms osteogenesis and ossification are often used synonymously to indicate the process of bone formation. Parts of the skeleton form during the …
Follow the formation of all blood cells from the pluripotent stem cells to the final formed elements. 14. Describe the stages of RBC development, the conditions and hormones that regulate their production through negative feedback, and nutrients required for their construction. 15. Identify the hemopoietic growth factors that regulate the differentiation and proliferation of particular
Bone formation 2 – Endochondral ossification The process of bone formation occurs in three stages, orchestrated by specialized bone cells that secrete and absorb materials as
The soft callus stage. Intramembraneous ossification forming bone cuffs away from the fracture gap. Replacement of the granulation tissue elsewhere in the callus by fibrous tissue and cartilage, and ingrowth of vessels into the calcified callus.
The skeleton consists of bone developing from mesoderm, except within the head where neural crest also contributes connective tissues. Each tissue (cartilage, bone, and skeletal muscle) goes through many different mechanisms of differentiation.
Endochondral ossification within the limb begins at Carnegie stage 18 and also occurs throughout embryo skeleton. This process is the replacement of a cartilage “template” with bone (week 5-12) that continues through postnatal development, with a second surge of growth at puberty.
1530 TVelnar,TBailey,VSmrkolj Anoverviewofthewoundhealingprocess as acute and chronic according to their time frame of healing. 3,5,6 ACUTEWOUNDS Wounds that repair
A baby goes through several stages of development, beginning as a fertilized egg. The egg develops into a blastocyst, an embryo, then a fetus. The egg develops into a blastocyst, an embryo, then a fetus.
The different stages of fracture healing are outlined below: haematoma: there is tissue damage and bleeding at the site of the fracture. There is death of bone …
The growing skull, mandible (jaw) and clavicle (collar bone) form directly from osteoblasts, and do not have a cartilage stage. A layer of cells which can differentiate into the osteoblasts lines the bone, with a special concentration between the bones of the skull.
Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest bone of the face, serves for the reception of the lower teeth. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles. For better description development of the mandible will be
200 Rev Odonto Cienc 2011;26(3):198-202 Bovine hydroxyapatite and bone formation Results On the first post-surgery day, CG1 and EG1 showed a dense fibrin network embracing the inorganic bovine
Review Bone Injury and Fracture Healing Biology
Stage IV is called terminal or end stage RA. The inflammatory process has subsided and formation of fibrous tissue and/or fusing of bone results in ceased joint function. This stage may be associated with formation of subcutaneous nodules.
95 Formation of Platelets and Thrombocytopenia MODULE Hematology and Blood Bank Technique HEMATOLOGY AND BLOOD BANK TECHNIQUE Notes Mature megakaryocytes or stageIII/IV megakaryocytes are very large cells,
2003 Armidale Feeder Steer School 21 On the other hand, severe restriction in Stage 1 results in impaired bone and muscle development – these calves don’t catch up when
osseointegration has been defined at multiple levels such as osteocytes extending 100-500 Ìm into the host bone3,11-13. Major stages of skeletal response to implantation-related injury and key histological events as related to the host response after insertion and mechanical fixation of cement-less implants include hematoma formation and mesenchymal tissue development, woven bone
BONE REMODELLING The process by which overall size and shape of bone is established- bone modelling. Embryo to pre-adult period. Rapidly formed on periosteal surface simultaneous destruction on endosteal surface at focal points and with in the osteon. Bone formation greater than resorption. Bone turnover or remodelling – replacement of old bone by new bone.
Describe the process of bone remodeling. Why does this process exist? Bone remodeling, in brief, is the process by which osteoclasts eat old bone and stimulate osteoblasts to make new bone.
Developmental stages of Myotis lucifugus are described and data on the sequence of post-cranial skeletogenesis are provided. A total of 27 embryonic, A total of 27 embryonic, We use cookies to enhance your experience on our website.
Early Stages of Bone Fracture Healing 157 Keywords Mathematical modeling of bone healing · Fibrin polymerization · Chemotaxis ·Early callus formation · Moving differentiation fronts
HIGH-RESOLUTION ANALYSIS OF HYPERGLYCEMIC BONE

Growth maturity and carcase specifications Community List
In the early stages of embryonic development, the embryo’s skeleton consists of fibrous membranes and hyaline cartilage. By the sixth or seventh week of embryonic life, the actual process of bone development, ossification (osteogenesis), begins.
Bone Development & Growth SEER Training

Development and growth of the mandible Dentistry Faculty
Musculoskeletal System Bone Development – Embryology


Chapter 1. Bone Embryology UCL
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone
Fracture Healing learnorthopaedics.com
– stages of bone formation SlideShare
BONE DEVELOPMENT AND ITS RELATION TO FRACTURE REPAIR.

(PDF) Early Stages of Bone Fracture Healing Formation of
A & P 1 Simplified Steps of Bone Formation Questions and

Fracture healing involves a complex and sequential set of events to restore injured bone to pre-fracture condition stem cells are crucial to the fracture repair process the …
Fracture healing Radiology Reference Article
Musculoskeletal System Bone Development Timeline
Physiology and Pathophysiology of Bone Remodeling Lawrence G. Raisz The skeleton is a metabolically active organ that under-goes continuous remodeling throughout life.
Stages of Intramembranous Ossification A Life Worthwhile
Fracture Healing Basic Science – Orthobullets
Bone Development Boundless Anatomy and Physiology