Bone development and growth pdf
Bone development and growth pdf
Androgens and bone Bart L. Clarkea,∗ Androgens likely stimulate longitudinal bone growth by their direct effects on growth plate chondrocytes. Under strict culture conditions, androgens regulate both prolifera- tion and differentiation of cultured epiphyseal chondrocytes [10]. Testosterone injected directly into the rat growth plate increases the width of the growth plate [26]. Part of
We have invited contributions that look at muscle and bone development from different angles. One of the Guest Editors sets the scene by looking at the question: How do bones get bigger?1 As it turns out, this funda-mental question so far has received mostly one-dimensional answers. There is a good deal of information on how growth pro-ceeds in a longitudinal direction, but much less is known
Endochondral ossification is essential for the formation of long bones (bones that are longer than they are wide, such as the femur, or thigh, bone and the humerus – the bone in your upper arm
Intramembranous ossification involves the proliferation of osteogenic cells within bone islands, which produces the flat bones of the face and clavicles. Endochondral ossification is the process by which the long bones of the body form, and is most commonly the way in which damaged adult bone heals (i.e., fracture healing). In endochondral ossification, cartilage serves as a precursor or
Analysis of skeletal maturation in patients aged 13 to 20 years by means of hand wrist radiographs Yasmine Bitencourt Emílio Mendes*, Juliana Roderjan Bergmann**, Marina Fonseca Pellissari**, Sérgio Paulo Hilgenberg***, Ulisses Coelho**** Objectives: Evaluate an alternative and simplified radiographic method that will enable implantologists and orthodontists to keep track of bone growth
children: physical, mental and intellectual development H Salome Kruger School of Physiology, Nutrition and Consumer Sciences North-West University (Potchefstroom Campus) INTRODUCTION A holistic approach is necessary to address the child’s overall development, including physical, mental, emotional and behavioural development Many factors impact on growth and development, but …
Growth is physical change and increase in size. It can be measured quantitatively. Indicators of growth include height, weight, bone size and dentition. The pattern of physiologic growth is similar for all people. However, growth rates vary during different stages of growth and development. The growth rate is rapid during the prenatal, neonatal, infancy and adolescent stages and slows during
The effect of growth hormone on bone is mostly mediated via insulin like growth hormone (IGF). There may however be a direct effect through growth hormone receptors on osteoblasts and chondrocytes. There may however be a direct effect through growth hormone receptors on …
Bone growth primarily occurs at the epiphyseal growth plates and is the result of the proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes. GH has direct effects on these chondrocytes, but primarily regulates this function through IGF-I, which stimulates the proliferation of and matrix production by these cells. GH deficiency severely limits bone growth and hence the accumulation of bone mass. GH
–Growth and strength in early adulthood, then slow process of decline afterwards –Decline affected by health and lifestyles . dr.Shaban 6 Cognitive Development in Early Adulthood Piaget believed that the formal operational stage (ages 11 to 15) is the highest stage of thinking Adults gain knowledge, but ways of thinking are the same as those of adolescents Some researchers disagree with
Bones that are longer than they are wide are called long bones. They consist of a long shaft with two bulky ends or extremities. They are primarily compact bone but may have a large amount of spongy bone at the ends or extremities. Long bones include bones of the thigh, leg, arm, and forearm.
quired for bone growth, bone remodeling, and bone repair in vertebrates is regulated by the availability of a subset of BMPs including BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, and -9.
As development of endochondral bones proceeds, chondro- cytes at the center of the avascular anlagen cease to proliferate and differentiate (in a process requiring Wnt signaling and
Most bones originate as hyaline cartilage which becomes ossified through the process of endochondral ossification. Figure 6-10a (steps 1-6) The growth and ossification of a long bone occurs in 6 steps:
Animal protein and bone growth – Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to animal protein and bone growth pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006[1] – Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies
While growth in cannon bone length stops with the fusion of both growth plates at around 1 ½ years of age, increase in cannon bone girth does not taper off until close to 5 years of age, and essentially the same can be said for the girth of any other limb element, with
The role of estrogen in bone growth and formation changes
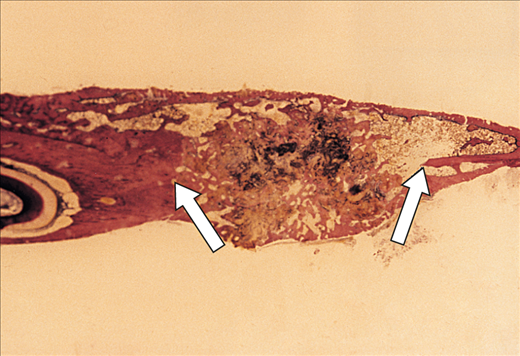
Analysis of skeletal maturation in patients aged 13 to 20
During growth, undernutrition, including insufficient caloric and protein intake, can severely impair bone development. Low protein intake lowers both the production and action of a growth factor called IGF-1, which enhances bone formation.
11. Describe the bone growth regulatory role of these hormones. a. Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs) – b. Human Growth Hormone (GH) – c. Estrogen, Testosterone, Thyroid Hormones, and Insulin –
Growth and remodeling of the human maxilla DONALD H. ENLOW, Prr.D., and SEOSG BANG, D.D.S. Ann Arbor, Mich. THE purpose of the present study is to describe and interpret the sequence of remodeling changes which take place during the postnatal growth of the young human maxilla. This report is a sequel to previous studies dealing with principles of bone remodeling and with the postnatal growth
(Bone 18:55-1OS; 1996) Key Words: Bone; Bone development; Bone adaptation; Mechanical adaptation; Mathematical modeling; Morphogenesis. Introduction The fertilization of the ovum results in a single cell with the necessary genetic information for the development of the entire organism. What follows is an extremely complicated orchestration of cell division, differentiation, growth, and
Osteoporosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality through its association with age-related fractures. Although most effort in fracture prevention has been directed at retarding the rate of
with bone growth and remodeling, resulting in decreased bone density and increased risk of fracture. Those effects may be exerted directly or indirectly through the many cell types, hormones, and growth factors that regulate bone metabolism. This article summarizes alcohol’s harmful effects on bone in both adults and adolescents. In addition, the article suggests possible physiological

Muscle and Bone Growth As children grow, muscle mass steadily increases throughout the developing years. At birth, approxi – mately 25% of a child’s body weight is muscle mass, and by adulthood about 40% of a person’s total body mass is muscle. During puberty, a 10-fold increase in testosterone production in boys results in a marked increase in muscle mass, whereas in girls an increase in
Joint Bone Spine 77 (2010) 517–518 Research lectures Roles o me Ryan C. R b a Department o reet, B b Veterans Adm a r t i c l Article history: Accepted 11 Ju Available…
Composition of bone • Calcium (Ca) accounts for much of the bone mass. • The Ca crystals give bone its strength – Hydroxyapatite, Ca 10(PO 4)
For appositional growth, the diameter of bones around the diaphysis grows by deposition of bone beneath the periosteum. From inside, the osteoclasts continue to resorb bone until its ultimate thickness is achieved. At this point the rate of formation on the outside and …
Evaluation of the bone age in 9-12 years old children in Manaus-AM city intROduCtiOn Two thirds of orthodontic patients have mal-occlusion in which growth and development play an important role in the success or failure of treat-ment and directly affect the decisions about the use of extraoral mechanics, functional appliances, extractions or even orthognathic surgeries. Ortho-dontists should
wt heterozygote Human heterozygote Human mutations in RUNX2 lead to cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) Otto et al. Cell, 1997 Mundlos et al. Cell, 1997
Factors affecting bone development, growth, and repair. A number of factors influence bone development, growth, and repair. These include nutrition, exposure to sunlight, hormonal secretions, and physical exercise. For example, vitamin D is necessary for proper absorption

During childhood, the long bones (in the arms, legs, and back) grow at the ends of the bones, whereas the flat bones (such as the skull) have a different pattern of growth. Adult bone actually continues to expand, although very slowly. Bone also continually undergoes remodeling, replacing old bone with new bone. Ordinary activity causes microscopic cracks in the bone, and these are dissolved
F. Rauch: Bone structure during puberty 2 Metaphyseal cortex Metaphyses are the most common sites of fracture during growth. For example, about 30% of childhood fractures affect
sexual development. They regulate growth, muscle, moods, brain- cognitive, feelings..hormones They regulate growth, muscle, moods, brain- cognitive, feelings..hormones most significantly plays a roll in bone growth and density this study says 70% more likely to get
Throughout fetal development and into childhood growth and development, bone forms on the cartilaginous matrix. By the time a fetus is born, most of the cartilage has been replaced with bone. Some additional cartilage will be replaced throughout childhood, and some cartilage remains in …
Hence, in this form of growth disorder, the potential normal bone growth (and therefore, body growth) is impaired, while skeletal age is not delayed or is delayed much less than is height.
The role of estrogen in bone growth and formation: changes at puberty Divya Singh1, Sabyasachi Sanyal2, Naibedya Chattopadhyay11Division of Endocrinology, 2Division of Drug Target Discovery and Development, Central Drug Research Institute (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research), Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, IndiaAbstract: A high peak bone
Bone Growth Regulation & Blood Calcium wiley.com
Embryonic Development of the Bone: Bones arise from three distinct lineages. The somites generate the axial skeleton, the lateral plate mesoderm generates the limb skeleton, and the cranial neural crest gives rise to the branchial arch and craniofacial bones and cartilage.
Recent longitudinal studies have found lean mass development to be the best predictor for BMC and areal density accrual during prepubertal growth in children, independent of the physical activity level.[20, 31] Although the latter studies do not exclude the fact that both bone and lean mass (muscle) development could be independently determined by genetic mechanisms, the muscle-bone
Ossification (or osteogenesis) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells called osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation.
In childhood growth and development targets are more often linked to bone age ra- ther than chronological age so this measurement is a good marker for long term growth.
Taurine (2-Amino ethane sulfonic acid) is a naturally occurring sulphur amino acid, found in several mammalian and non mammalian tissues. Taurine is believed to be involved in several life processes. – bone loss and patterns of bone destruction pdf Bone development occurs either embryonically or postembryonically. Embryonic development is when cells differentiate and form new tissues and organs.
Bone age, malnutrition, growth hormone, hypothyroidism, short stature Bright Futures Core Concepts: While all of the Core Concepts are included in each case, this particular case can be used to
stages of bone formation 1. Growth andGrowth and Development of BoneDevelopment of Bone 2. IntroductionIntroduction Bone is a relatively hard and lightweightBone is a relatively hard and lightweight composite material, formed mostly ofcomposite material, formed mostly of calcium phosphatecalcium phosphate Bone
Chondrocytes and Longitudinal Bone Growth: The Development of Tibial Dyschondroplasia C. Farquharson1 and D. Jefferies Bone Biology Group, Division of …
55 F Shapiro Bone development and fracture repair The growth plate components go through a sequential process of cell proliferation, synthesis of extracellular ma-
644 Sunlight on Bone of Swine rate of growth. In other respects the rations are believed to be adequate for the growth and normal development of swine with
Objective: To study the acquisition of bone mass and changes in bone mineral density (BMD) related to age, bone age, pubertal status, and growth hormone (GH) therapy in 11 children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) longitudinally over 4 years, in comparison to healthy children.
A morphogenetic analysis of facial growth DONALD H. ENLOW, PH.D. Ann Arbor, M&h. angular changes and relative distances moved during the growth of different bones or parts of bones. It is known, however, that actual directions of growth often do not correspond with such apparent growth movements, since a process of “forward thrust” is involved in both maxillary and mandibular growth
Mammalian growth plate, also known as epiphyseal plate or physis, is highly specialized mesoderm- derived cartilaginous structure. It develops in the bone bud, secondary to presence of the primary ossification centers and is responsible for bone elongation. The plates are formed by numerous cells that rapidly divide and mature. Post puberty, the epiphyseal cartilage cell division decreases
10/02/2016 · The skeleton is an exquisitely sensitive and archetypal T 3-target tissue that demonstrates the critical role for thyroid hormones during development, linear growth, and adult bone …
intramembranous and endochondrial bone development. GROWTH (NOTE: BONE HAS NO INTERSITIAL GROWTH AS DOES CARTILAGE) COMPACT BONE-SHAFT AND OUTER SURFACE OF LONG BONES ENDOSTEUM – INSIDE COMPACT BONE, SURFACES OF SPONGY BONE, INSIDE HAVERSIAN SYSTEMS . COMPACT BONE HAVERSIAN SYSTEMS – LAMELLAE OF BONE AROUND HAVERSIAN CANAL LINKED BY VOLKMANN’S CANAL. Slide 19: Compact bone …
Hormones involved in bone growth (hormone – gland – function) Growth hormone – anterior pituitary gland – increases the rate of mitosis of chondrocytes and osteoblasts, and increases the rate of protein synthesis (collagen, cartilage matrix, and enzymes for cartilage and bone formation)
GROWTH AND BONE AGE CAH is us
tissue than it appears to be upon casual observation; however, com-plete bone mineralization lags behind growth in height and weight. Height or long bone growth is the
Bones are an important part of the human body, and their development and growth is a carefully regulated process that depends on the interactions of various cells, hormones, and vitamins.
Role of Thyroid Hormones in Skeletal Development and Bone

Roles of vessel growth factors in bone development and
Bone Development and Growth hannasd.org

Regulating Bone Growth and Development with Bone
How does Exercise Affect Bone Development during Growth


A morphogenetic analysis of facial growth Deep Blue
Bone development and skeletal growth eiseverywhere.com
road king shop manual download – Muscle and Bone Growth Developmental Open University
Hormones and Bone Growth Innvista


TIMING AND RATE OF SKELETAL MATURATION IN HORSES With
Growth and bone development Request PDF ResearchGate
BONE DEVELOPMENT AND ITS RELATION TO FRACTURE REPAIR.
Principles of Sound Growth morganequine.com
Bones are an important part of the human body, and their development and growth is a carefully regulated process that depends on the interactions of various cells, hormones, and vitamins.
Factors affecting bone development, growth, and repair. A number of factors influence bone development, growth, and repair. These include nutrition, exposure to sunlight, hormonal secretions, and physical exercise. For example, vitamin D is necessary for proper absorption
Hence, in this form of growth disorder, the potential normal bone growth (and therefore, body growth) is impaired, while skeletal age is not delayed or is delayed much less than is height.
Osteoporosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality through its association with age-related fractures. Although most effort in fracture prevention has been directed at retarding the rate of
Chondrocytes and Longitudinal Bone Growth: The Development of Tibial Dyschondroplasia C. Farquharson1 and D. Jefferies Bone Biology Group, Division of …
While growth in cannon bone length stops with the fusion of both growth plates at around 1 ½ years of age, increase in cannon bone girth does not taper off until close to 5 years of age, and essentially the same can be said for the girth of any other limb element, with
Composition of bone • Calcium (Ca) accounts for much of the bone mass. • The Ca crystals give bone its strength – Hydroxyapatite, Ca 10(PO 4)
Joint Bone Spine 77 (2010) 517–518 Research lectures Roles o me Ryan C. R b a Department o reet, B b Veterans Adm a r t i c l Article history: Accepted 11 Ju Available…
Androgens and bone Bart L. Clarkea,∗ Androgens likely stimulate longitudinal bone growth by their direct effects on growth plate chondrocytes. Under strict culture conditions, androgens regulate both prolifera- tion and differentiation of cultured epiphyseal chondrocytes [10]. Testosterone injected directly into the rat growth plate increases the width of the growth plate [26]. Part of
Analysis of skeletal maturation in patients aged 13 to 20
Bone Structure Development and Bone Biology SpringerLink
Chondrocytes and Longitudinal Bone Growth: The Development of Tibial Dyschondroplasia C. Farquharson1 and D. Jefferies Bone Biology Group, Division of …
Bone age, malnutrition, growth hormone, hypothyroidism, short stature Bright Futures Core Concepts: While all of the Core Concepts are included in each case, this particular case can be used to
Analysis of skeletal maturation in patients aged 13 to 20 years by means of hand wrist radiographs Yasmine Bitencourt Emílio Mendes*, Juliana Roderjan Bergmann**, Marina Fonseca Pellissari**, Sérgio Paulo Hilgenberg***, Ulisses Coelho**** Objectives: Evaluate an alternative and simplified radiographic method that will enable implantologists and orthodontists to keep track of bone growth
sexual development. They regulate growth, muscle, moods, brain- cognitive, feelings..hormones They regulate growth, muscle, moods, brain- cognitive, feelings..hormones most significantly plays a roll in bone growth and density this study says 70% more likely to get
Mammalian growth plate, also known as epiphyseal plate or physis, is highly specialized mesoderm- derived cartilaginous structure. It develops in the bone bud, secondary to presence of the primary ossification centers and is responsible for bone elongation. The plates are formed by numerous cells that rapidly divide and mature. Post puberty, the epiphyseal cartilage cell division decreases
55 F Shapiro Bone development and fracture repair The growth plate components go through a sequential process of cell proliferation, synthesis of extracellular ma-
quired for bone growth, bone remodeling, and bone repair in vertebrates is regulated by the availability of a subset of BMPs including BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, and -9.
In childhood growth and development targets are more often linked to bone age ra- ther than chronological age so this measurement is a good marker for long term growth.
F. Rauch: Bone structure during puberty 2 Metaphyseal cortex Metaphyses are the most common sites of fracture during growth. For example, about 30% of childhood fractures affect
The necessity for a balanced diet in children physical
stages of bone formation SlideShare
During childhood, the long bones (in the arms, legs, and back) grow at the ends of the bones, whereas the flat bones (such as the skull) have a different pattern of growth. Adult bone actually continues to expand, although very slowly. Bone also continually undergoes remodeling, replacing old bone with new bone. Ordinary activity causes microscopic cracks in the bone, and these are dissolved
wt heterozygote Human heterozygote Human mutations in RUNX2 lead to cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) Otto et al. Cell, 1997 Mundlos et al. Cell, 1997
11. Describe the bone growth regulatory role of these hormones. a. Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs) – b. Human Growth Hormone (GH) – c. Estrogen, Testosterone, Thyroid Hormones, and Insulin –
Muscle and Bone Growth As children grow, muscle mass steadily increases throughout the developing years. At birth, approxi – mately 25% of a child’s body weight is muscle mass, and by adulthood about 40% of a person’s total body mass is muscle. During puberty, a 10-fold increase in testosterone production in boys results in a marked increase in muscle mass, whereas in girls an increase in
Bone growth primarily occurs at the epiphyseal growth plates and is the result of the proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes. GH has direct effects on these chondrocytes, but primarily regulates this function through IGF-I, which stimulates the proliferation of and matrix production by these cells. GH deficiency severely limits bone growth and hence the accumulation of bone mass. GH
Osteoporosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality through its association with age-related fractures. Although most effort in fracture prevention has been directed at retarding the rate of
In childhood growth and development targets are more often linked to bone age ra- ther than chronological age so this measurement is a good marker for long term growth.
F. Rauch: Bone structure during puberty 2 Metaphyseal cortex Metaphyses are the most common sites of fracture during growth. For example, about 30% of childhood fractures affect
Joint Bone Spine 77 (2010) 517–518 Research lectures Roles o me Ryan C. R b a Department o reet, B b Veterans Adm a r t i c l Article history: Accepted 11 Ju Available…
Bones are an important part of the human body, and their development and growth is a carefully regulated process that depends on the interactions of various cells, hormones, and vitamins.
As development of endochondral bones proceeds, chondro- cytes at the center of the avascular anlagen cease to proliferate and differentiate (in a process requiring Wnt signaling and
quired for bone growth, bone remodeling, and bone repair in vertebrates is regulated by the availability of a subset of BMPs including BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, and -9.
Endochondral ossification is essential for the formation of long bones (bones that are longer than they are wide, such as the femur, or thigh, bone and the humerus – the bone in your upper arm
Hence, in this form of growth disorder, the potential normal bone growth (and therefore, body growth) is impaired, while skeletal age is not delayed or is delayed much less than is height.
Effect of Hormones on Bone Development Annual Review of
Bone (Osseous tissue)Bone (Osseous tissue) Cuyamaca College
Composition of bone • Calcium (Ca) accounts for much of the bone mass. • The Ca crystals give bone its strength – Hydroxyapatite, Ca 10(PO 4)
(Bone 18:55-1OS; 1996) Key Words: Bone; Bone development; Bone adaptation; Mechanical adaptation; Mathematical modeling; Morphogenesis. Introduction The fertilization of the ovum results in a single cell with the necessary genetic information for the development of the entire organism. What follows is an extremely complicated orchestration of cell division, differentiation, growth, and
Growth and remodeling of the human maxilla DONALD H. ENLOW, Prr.D., and SEOSG BANG, D.D.S. Ann Arbor, Mich. THE purpose of the present study is to describe and interpret the sequence of remodeling changes which take place during the postnatal growth of the young human maxilla. This report is a sequel to previous studies dealing with principles of bone remodeling and with the postnatal growth
Analysis of skeletal maturation in patients aged 13 to 20 years by means of hand wrist radiographs Yasmine Bitencourt Emílio Mendes*, Juliana Roderjan Bergmann**, Marina Fonseca Pellissari**, Sérgio Paulo Hilgenberg***, Ulisses Coelho**** Objectives: Evaluate an alternative and simplified radiographic method that will enable implantologists and orthodontists to keep track of bone growth
11. Describe the bone growth regulatory role of these hormones. a. Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs) – b. Human Growth Hormone (GH) – c. Estrogen, Testosterone, Thyroid Hormones, and Insulin –
Throughout fetal development and into childhood growth and development, bone forms on the cartilaginous matrix. By the time a fetus is born, most of the cartilage has been replaced with bone. Some additional cartilage will be replaced throughout childhood, and some cartilage remains in …
We have invited contributions that look at muscle and bone development from different angles. One of the Guest Editors sets the scene by looking at the question: How do bones get bigger?1 As it turns out, this funda-mental question so far has received mostly one-dimensional answers. There is a good deal of information on how growth pro-ceeds in a longitudinal direction, but much less is known
quired for bone growth, bone remodeling, and bone repair in vertebrates is regulated by the availability of a subset of BMPs including BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, and -9.
intramembranous and endochondrial bone development. GROWTH (NOTE: BONE HAS NO INTERSITIAL GROWTH AS DOES CARTILAGE) COMPACT BONE-SHAFT AND OUTER SURFACE OF LONG BONES ENDOSTEUM – INSIDE COMPACT BONE, SURFACES OF SPONGY BONE, INSIDE HAVERSIAN SYSTEMS . COMPACT BONE HAVERSIAN SYSTEMS – LAMELLAE OF BONE AROUND HAVERSIAN CANAL LINKED BY VOLKMANN’S CANAL. Slide 19: Compact bone …
Muscle and Bone Growth As children grow, muscle mass steadily increases throughout the developing years. At birth, approxi – mately 25% of a child’s body weight is muscle mass, and by adulthood about 40% of a person’s total body mass is muscle. During puberty, a 10-fold increase in testosterone production in boys results in a marked increase in muscle mass, whereas in girls an increase in
Taurine (2-Amino ethane sulfonic acid) is a naturally occurring sulphur amino acid, found in several mammalian and non mammalian tissues. Taurine is believed to be involved in several life processes.
Objective: To study the acquisition of bone mass and changes in bone mineral density (BMD) related to age, bone age, pubertal status, and growth hormone (GH) therapy in 11 children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) longitudinally over 4 years, in comparison to healthy children.
As development of endochondral bones proceeds, chondro- cytes at the center of the avascular anlagen cease to proliferate and differentiate (in a process requiring Wnt signaling and
Regulating Bone Growth and Development with Bone
How does Exercise Affect Bone Development during Growth
The effect of growth hormone on bone is mostly mediated via insulin like growth hormone (IGF). There may however be a direct effect through growth hormone receptors on osteoblasts and chondrocytes. There may however be a direct effect through growth hormone receptors on …
Analysis of skeletal maturation in patients aged 13 to 20 years by means of hand wrist radiographs Yasmine Bitencourt Emílio Mendes*, Juliana Roderjan Bergmann**, Marina Fonseca Pellissari**, Sérgio Paulo Hilgenberg***, Ulisses Coelho**** Objectives: Evaluate an alternative and simplified radiographic method that will enable implantologists and orthodontists to keep track of bone growth
with bone growth and remodeling, resulting in decreased bone density and increased risk of fracture. Those effects may be exerted directly or indirectly through the many cell types, hormones, and growth factors that regulate bone metabolism. This article summarizes alcohol’s harmful effects on bone in both adults and adolescents. In addition, the article suggests possible physiological
Bones that are longer than they are wide are called long bones. They consist of a long shaft with two bulky ends or extremities. They are primarily compact bone but may have a large amount of spongy bone at the ends or extremities. Long bones include bones of the thigh, leg, arm, and forearm.
Hence, in this form of growth disorder, the potential normal bone growth (and therefore, body growth) is impaired, while skeletal age is not delayed or is delayed much less than is height.
For appositional growth, the diameter of bones around the diaphysis grows by deposition of bone beneath the periosteum. From inside, the osteoclasts continue to resorb bone until its ultimate thickness is achieved. At this point the rate of formation on the outside and …
In childhood growth and development targets are more often linked to bone age ra- ther than chronological age so this measurement is a good marker for long term growth.
Chondrocytes and Longitudinal Bone Growth: The Development of Tibial Dyschondroplasia C. Farquharson1 and D. Jefferies Bone Biology Group, Division of …
–Growth and strength in early adulthood, then slow process of decline afterwards –Decline affected by health and lifestyles . dr.Shaban 6 Cognitive Development in Early Adulthood Piaget believed that the formal operational stage (ages 11 to 15) is the highest stage of thinking Adults gain knowledge, but ways of thinking are the same as those of adolescents Some researchers disagree with
Muscle and Bone Growth As children grow, muscle mass steadily increases throughout the developing years. At birth, approxi – mately 25% of a child’s body weight is muscle mass, and by adulthood about 40% of a person’s total body mass is muscle. During puberty, a 10-fold increase in testosterone production in boys results in a marked increase in muscle mass, whereas in girls an increase in
Joint Bone Spine 77 (2010) 517–518 Research lectures Roles o me Ryan C. R b a Department o reet, B b Veterans Adm a r t i c l Article history: Accepted 11 Ju Available…
stages of bone formation 1. Growth andGrowth and Development of BoneDevelopment of Bone 2. IntroductionIntroduction Bone is a relatively hard and lightweightBone is a relatively hard and lightweight composite material, formed mostly ofcomposite material, formed mostly of calcium phosphatecalcium phosphate Bone

The effect of growth hormone on bone is mostly mediated via insulin like growth hormone (IGF). There may however be a direct effect through growth hormone receptors on osteoblasts and chondrocytes. There may however be a direct effect through growth hormone receptors on …
TIMING AND RATE OF SKELETAL MATURATION IN HORSES With
quired for bone growth, bone remodeling, and bone repair in vertebrates is regulated by the availability of a subset of BMPs including BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, and -9.
Clarke 09 Androgens and bone Steroids HormoneBalance.org
Bone development and skeletal growth eiseverywhere.com
Effect of Hormones on Bone Development Annual Review of
quired for bone growth, bone remodeling, and bone repair in vertebrates is regulated by the availability of a subset of BMPs including BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, and -9.
stages of bone formation SlideShare
Bone Development and Stem Cells – LifeMap Discovery
Most bones originate as hyaline cartilage which becomes ossified through the process of endochondral ossification. Figure 6-10a (steps 1-6) The growth and ossification of a long bone occurs in 6 steps:
Effects of spay neuter programs on pets hormones bone